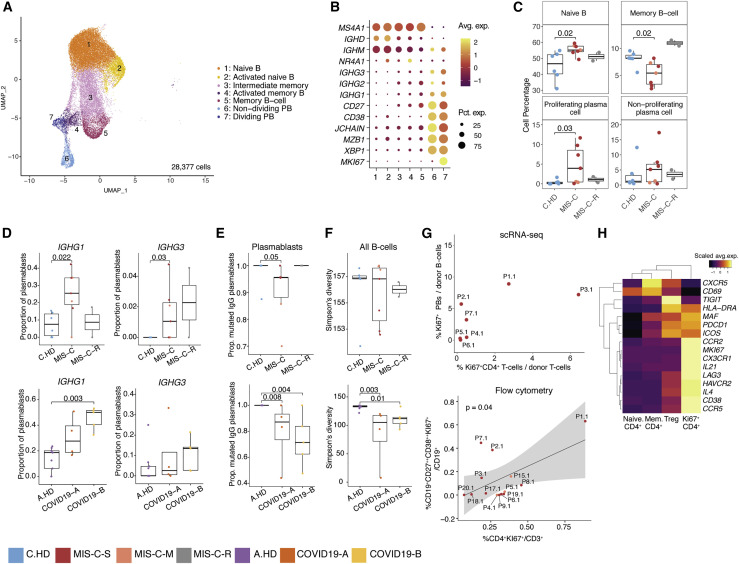
Figure 5.
MIS-C patients have increased proliferating plasmablasts harboring IgG1 and IgG3 and a coordinated CD4+ T cell response
(A) B cell sub-clustering UMAP.
(B) Dot plots for key B cell markers delineating naive, memory, and plasmablast subsets.
(C) Distributions of B cell frequencies within total B cells across donors. Two-sided Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used to calculate significance.
(D) IGHG1 and IGHG3 isotype frequencies as a proportion of plasmablasts (proliferating and non-proliferating) are depicted across donors. Statistical significance was calculated as in (C).
(E) Proportion mutated IGHG clones in plasmablasts. Statistical significance was calculated as in (C).
(F) Simpson’s diversity in all B cells computed across cohorts in pediatric cohorts (top) and adult cohorts (bottom). Significance calculated as above. Statistical significance was calculated as in (C).
(G) (Top): Percentage dividing plasmablasts/total B cells versus percentage Ki67+CD4+ cells/total T cells within the MIS-C cohort using scRNA-seq. Ki67+ CD4+ cells defined as CD4+ cells within the Ki67+ NK and T cell cluster (see Figure 4A). (Bottom): Correlation of dividing plasmablasts (CD272+CD382+Ki67+) among CD19+ B cells and Ki67+ CD4+ T cells among CD3+ T cells assessed by flow cytometry. Statistical significance calculated by linear regression. 95% confidence interval is shown in gray shading.
(H) Heatmap showing differential gene expression across four subsets of CD4+ T cells, comprising samples from the MIS-C scRNA-seq cohort. Scale bar represents the scaled average expression of markers.