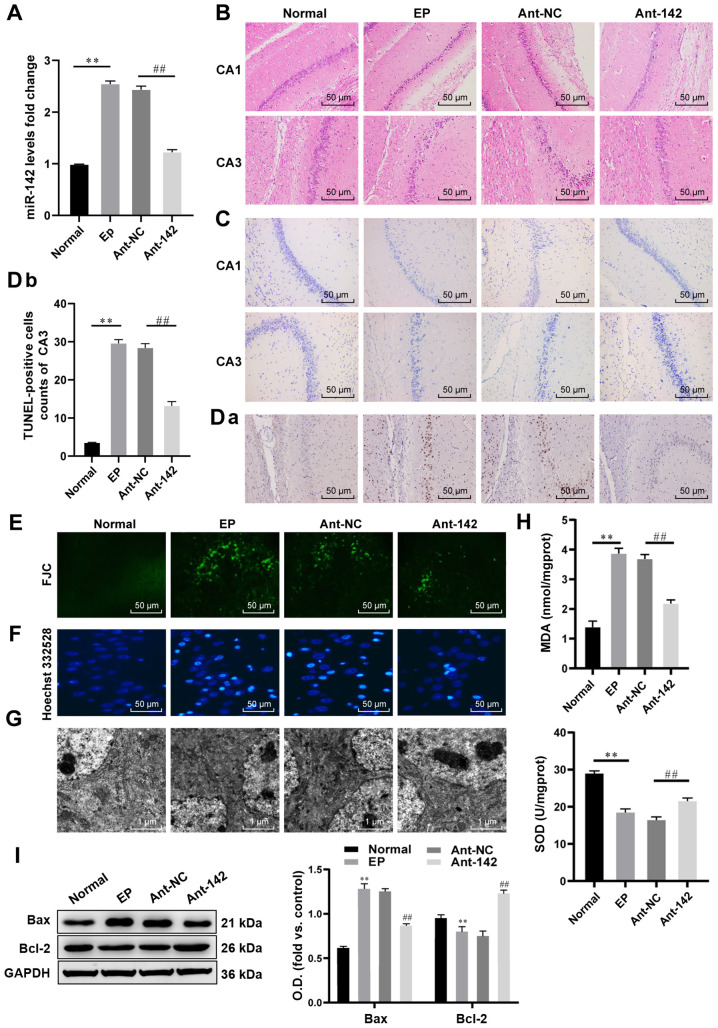
Figure 2.
miR-142 inhibition reduces ROS and apoptosis in hippocampal neurons in epileptic rats. (A) Relative miR-142 expression in normal rats and epileptic rats measured by RT-qPCR, n=3. (B and C) Representative images of the histopathological sections of the hippocampus in epileptic rats detected by H&E staining and Nissl staining, n=6. (D-F) Representative images of apoptosis and degeneration in the hippocampal CA3 region of epileptic rats detected by the TUNEL assay, FJC staining and Hoechst 332528 staining, n=6. (G) Representative images of the neuron structure in the hippocampus of epileptic rats observed under TEM, n=3. (H) Relative MDA and SOD contents in normal rats and epileptic rats measured by the TBA and WST-8 methods, n=3. (I) Protein levels of Bcl-2 and Bax in the hippocampus of normal rats and epileptic rats measured by western blot analysis, n=3. The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparisons test as a post hoc test. **P<0.01, compared with the normal group; ##P<0.01, compared with the antagomir-NC group. miR-142, microRNA-142; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick end labeling; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; FJC, Fluoro-Jade C; MDA, malondialdehyde; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TBA, thiobarbituric acid; WST-8, water-soluble tetrazolium salt-8; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma-2; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X; ANOVA, analysis of variance.