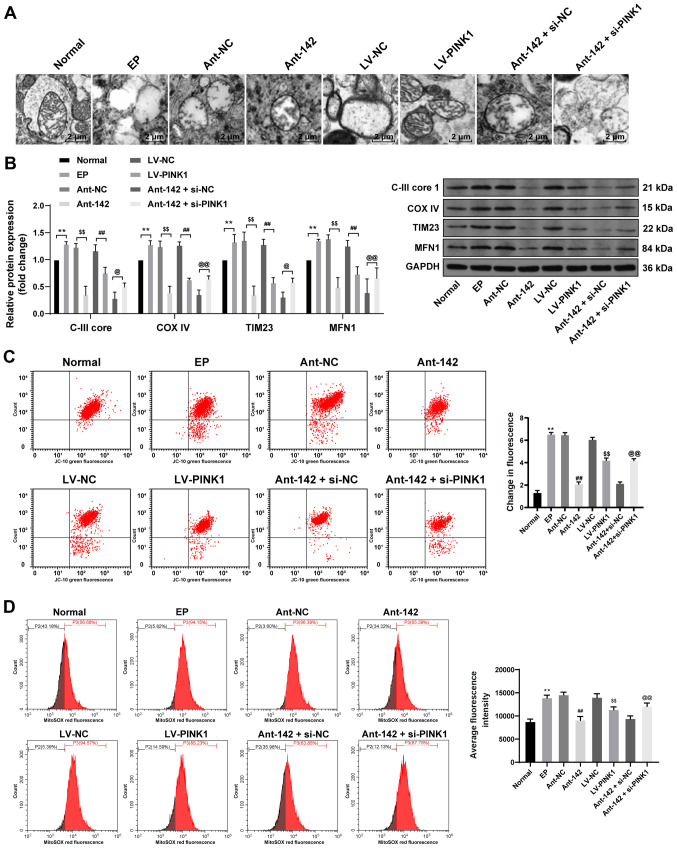
Figure 5.
miR-142 inhibition promotes mitochondrial autophagy in epileptic rats by upregulating PINK1. (A) Representative images of the mitochondrial structure in the hippocampus of epileptic rats were observed by TEM, n=3. (B) Protein levels of C-III core 1, COX IV, TIM23 and MFN1 in the hippocampus of epileptic rats were measured by western blot analysis, n=3; (C and D) Relative MTP and ROS generation in the hippocampus of epileptic rats were measured by JC-10 staining and MitoSOX-based flow cytometry, n=3. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, and pairwise comparisons following ANOVA were analyzed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test. **P<0.01, compared with the normal group; ##P<0.01, compared with the LV-NC group; $$P<0.01, compared with the antagomir-NC group; @P<0.05, @@P<0.01, compared with the antagomir-miR-142 + siRNA-NC group. miR-142, microRNA-142; PINK1, phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN)-induced putative kinase 1; TEM, transmission electron microscope; COX IV, cytochrome C oxidase IV; TIM23, translocase of the inner membrane 23; MFN1, mitochondrial fusion protein 1; MTP, mitochondrial transmembrane potential; ROS, reactive oxygen species; ANOVA, analysis of variance; LV, lentivirus vector; NC, negative control.