Figure 2.
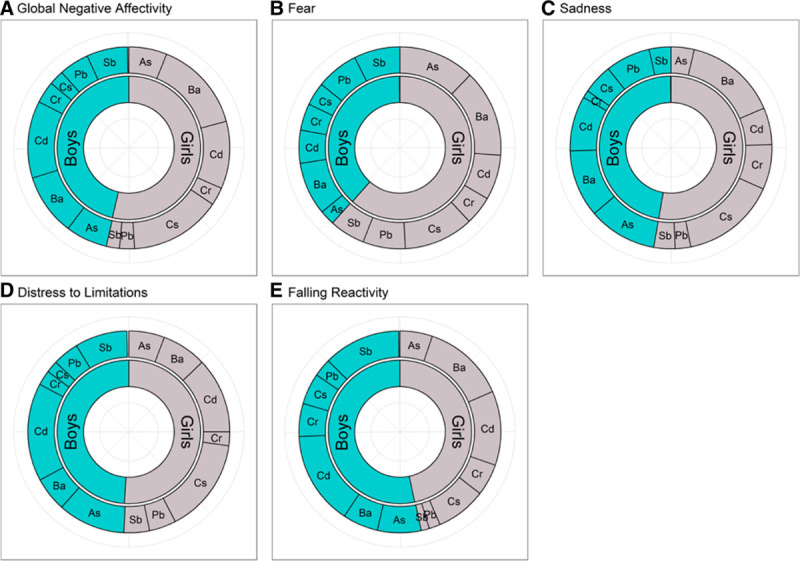
Metal mixture weights for the global and subdomains of infant negative affect (Fear, Sadness, Distress to Limitations, Falling Reactivity), stratified by infant sex. Values represent the mean weights across 100 repeated holdouts. Higher negative affect is characterized by higher scores on the global negative affectivity domain score and on the Fear, Sadness, and Distress to Limitations scales, and lower scores on the Falling Reactivity scale. Models are adjusted for: infant age at IBQ-R assessment (days), gestational week of urine collection (weeks), creatinine (mg/dL), maternal age (years), race/ethnicity (non-Hispanic White or other vs. Black/Hispanic-Black vs. Hispanic/non-Black), smoke exposure (yes vs. no as described in manuscript), and maternal education (less than high school degree vs. high school degree or more). As indicates arsenic; Ba, barium; Cd, cadmium; Cr, chromium; Cs, cesium; IBQ-R, Infant Behavior Questionnaire-Revised; Pb, lead; Sb, antimony.
