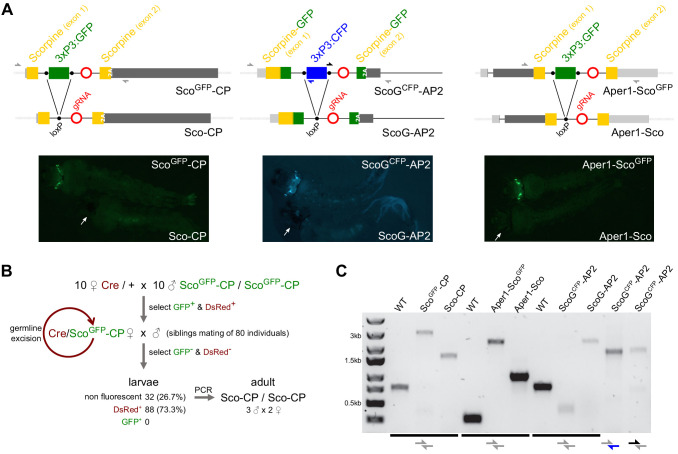
Figure 2. Generation of minimal genetic modifications.
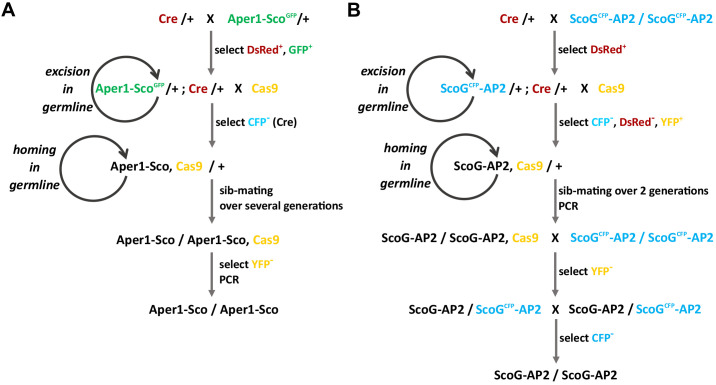
(A) Schematic showing the inserted transgene constructs within the exon structure of the CP, AP2, and Aper1 loci prior and following the excision of the marker gene by Cre recombinase (top) and the observed changes in green or cyan fluorescence in L3 larvae (bottom). Half arrows indicate primers for the PCRs shown in panel C and white arrows indicate the eyes in the markerless individuals. 2A indicates the F2A self-cleaving peptide signal. (B) Crossing scheme used for the establishment of markerless strain Sco-CP by crossing to a Cre recombinase expressing strain. Non-fluorescent adults were allowed to hatch individually, and their pupal cases were used for genotyping. (C) PCR genotyping of genomic DNA of homozygous individuals of all strains with primer-pairs (shown in A) spanning the three loci. The entire locus could not be amplified in strain ScoGCFP-AP2 that contains both GFP and CFP, and hence separate 5’ and 3’ fragments were analysed by PCR.