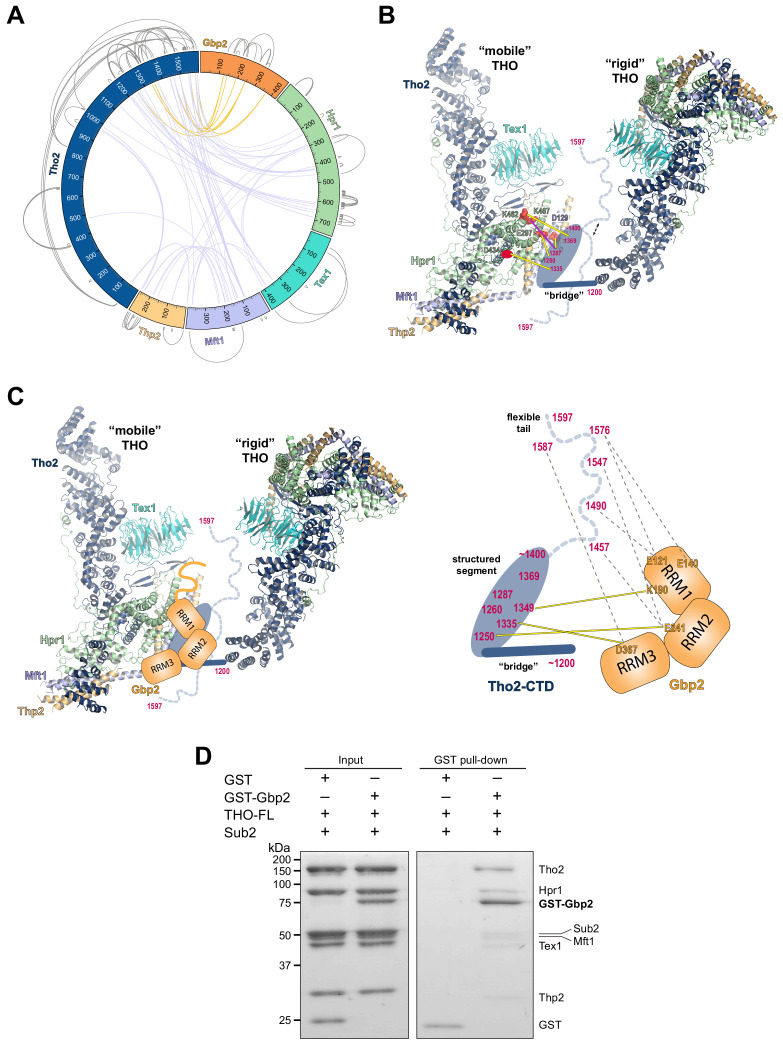
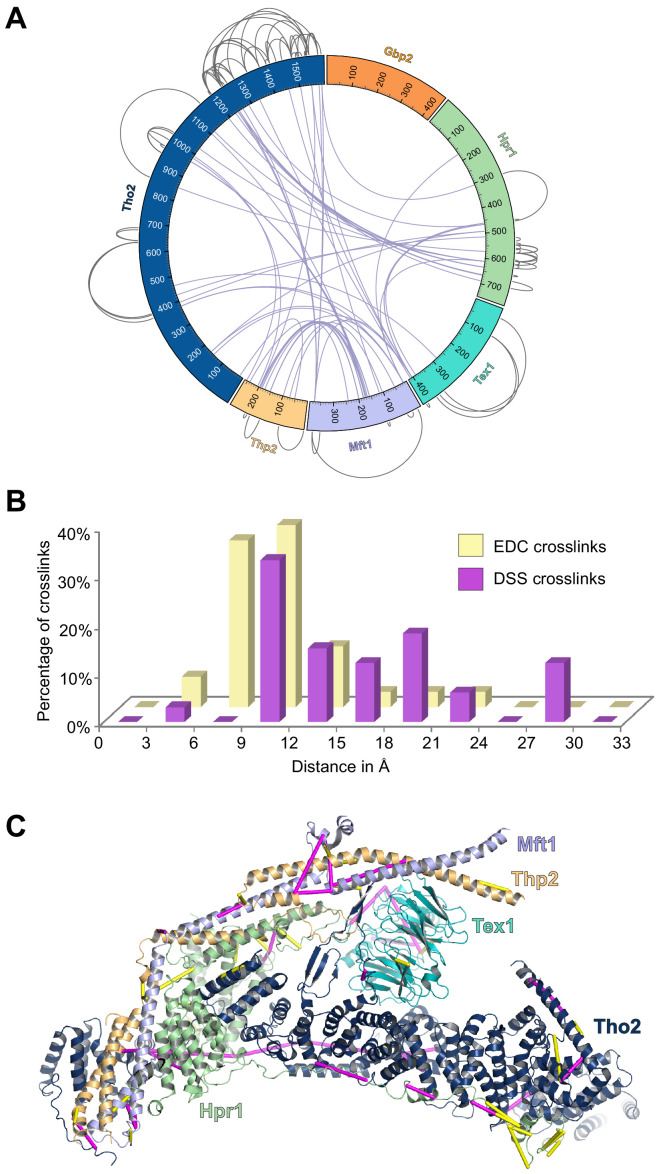
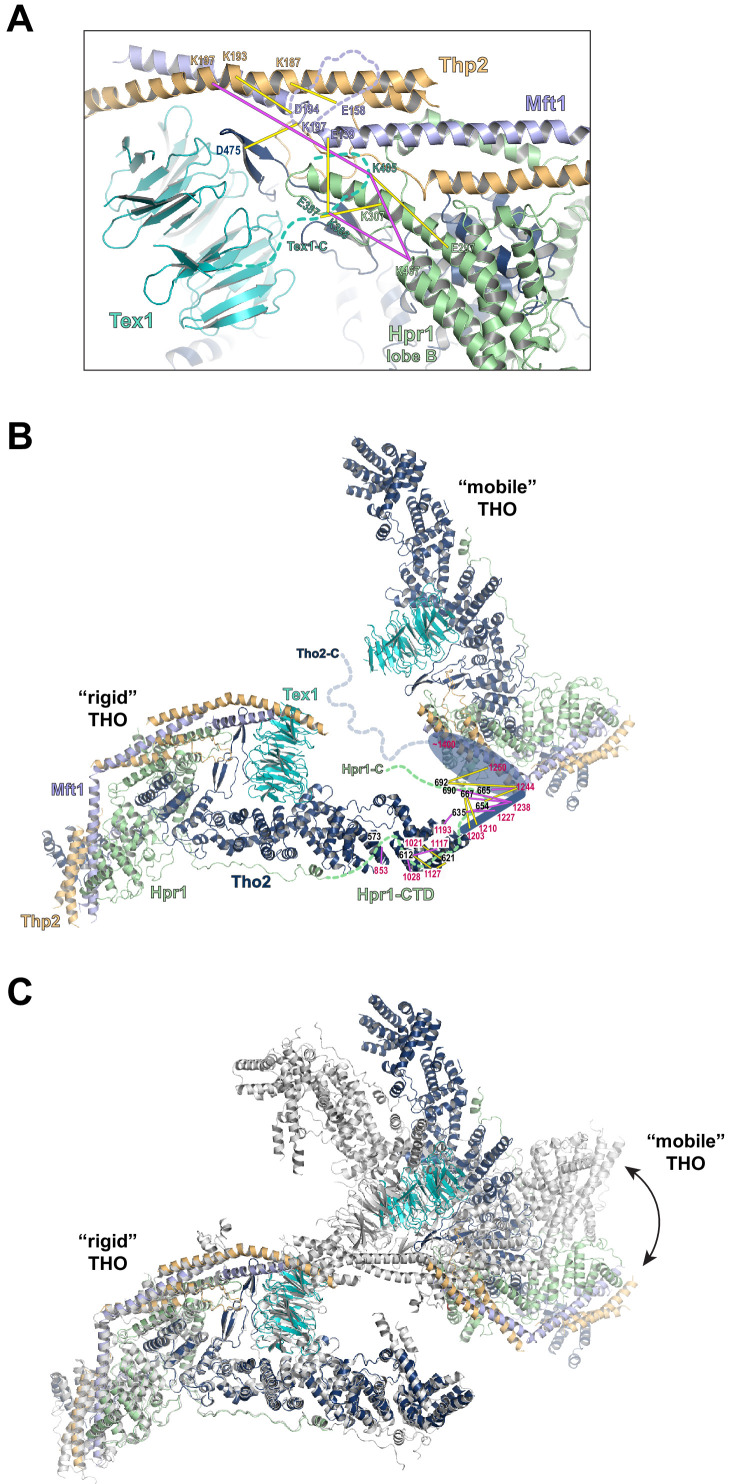
Figure 4. Chemical cross-linking and mass spectrometry reveals THO–Gbp2 interactions.
(A) Circular plot showing the cross-linking sites with EDC cross-linker. Each THO•Gbp2 complex subunit is represented as a colored segment with the amino acid residues indicated. Intermolecular cross-links are mapped inside the circle and the intramolecular cross-links are mapped outside the circle. The cross-links between Tho2 and Gbp2 are colored in orange. (B) Schematics of the arrangement of the Tho2–CTD, which contains a ‘bridge’ connecting two THO molecules, followed by a structured segment and a flexible tail (residues ~1400–1597). The EDC cross-links between the structured Tho2–CTD fragment and Hpr1 (E297, D434, and K462) as well as Mft1 (D129) are indicated by yellow lines. The DSS cross-link between Tho2–CTD and Hpr1–K467 is indicated by a purple line. (C) Schematics of the THO–Gbp2 interactions (left) and the identified cross-linking sites between Tho2–CTD and Gbp2 RRM domains. (D) In vitro GST-pull downs show that Gbp2 binds to the THO•Sub2 complex.