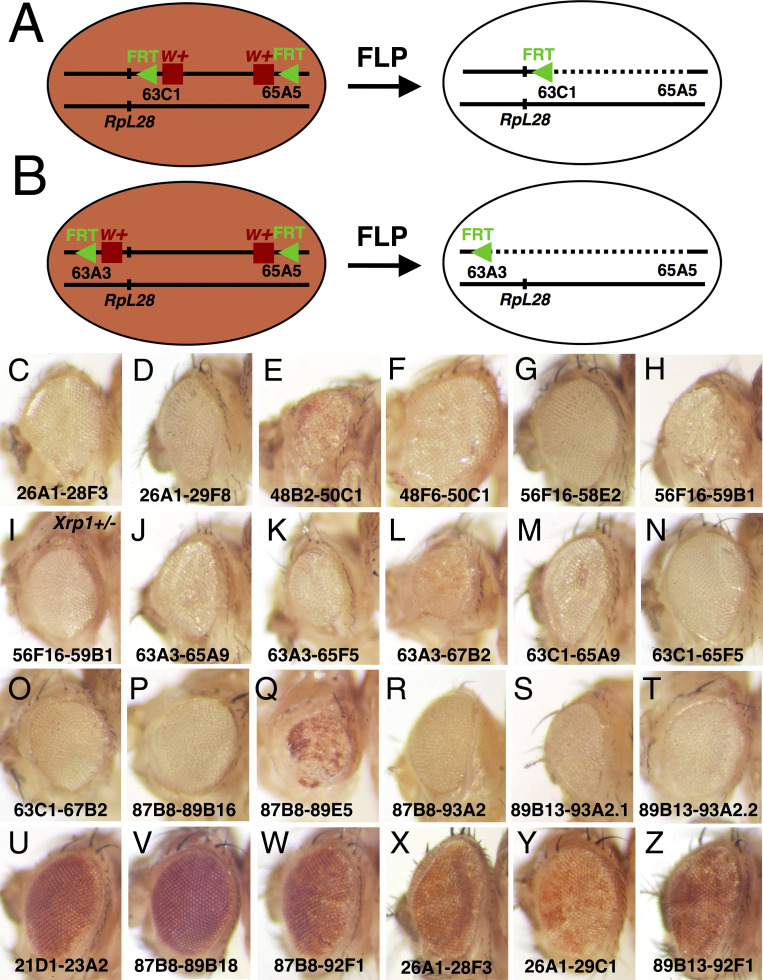
Figure 2. Generating segmental aneuploidy with Flp-FRT recombination.
(A) Segmental aneuploidy can be generated in a mosaic fashion using FLP-FRT. At left is a cell carrying two transposable elements encoding w+ and FRT, arranged in cis on one chromosome arm, in this case at chromosome bands 63C1 and 65A9, respectiely. (B) FLP-mediated recombination between FRT sites excising the intervening sequences. In this example, where the w+ genes lie between the FRT sites, both are excised resulting in a loss of eye pigmentation. The RpL28 gene at chromosome band 63B14 lies outside the deletion and is unaffected. (B) A comparable recombination between elements at chromosome bands 63A3-65A9 also deletes the RpL28 locus, so that the resulting segmentally aneuploid cells are heterozygously deleted for this gene. These cartoons show recombination in G1-phase of the cell cycle. In the G2-phase configuration, recombination between non-homologous FRT sites on the chromatids can occur leading to a deleted chromatid and a chromatid bearing 3 FRT insertion elements and a duplication of the intervening region. Such genotypes are substrates for further FLP recombination to the parental or deleted state, but sometimes we see them persist in adults and an example is shown in Figure 3D (Titen et al., 2020). Panels C-Z show adult eyes in the presence of eyFlp, which drives recombination close to completion in the eye and head, with the chromosome positions of parental w+ FRT insertions indicated. Panels C-T show genotypes where eyFlp recombined most eye cells, Panels U-Z illustrate genotypes where it did not. Strains that were poor substrates for Flp, either retained the parental eye color in the presence of eyFlp, or produce a salt and pepper pattern of very small clones that is indicative of excision occurring only late in development once large cell numbers are present. See Supplementary file 1 for more details and further genotypic information. (C) y w eyFlp; P{XP}d08241 PBac{WH}f04888/+; (D) y w eyFlp; P{XP}d08241 PBac{WH}f00857/+. This recombination deletes the RpL36A and RpS13 genes; (E) y w eyFlp; P{XP}d09761 PBac{WH}f00157/+. This recombination deletes the RpS11 gene. Note the particularly small size of the recombinant heads; (F) y w eyFlp; P{XP}d09417 PBac{WH}f00157/+. (G) y w eyFlp; P{XP}d02302 PBac{WH}f04349/+; (H) y w eyFlp; P{XP}d02302 PBac{WH}f00464/+. This recombination deletes the RpS16 and RpS24 genes. Note the particularly small size of the recombinant heads; (I) y w eyFlp; P{XP}d02302 PBac{WH}f00464/Xrp1m2-73. Eye size is partially rescued by heterozygosity for Xrp1. (J) y w eyF; PBac{WH}f01922 P{XP}d02570 /+. This recombination deletes the RpL28 gene. (K) y w eyF; PBac{WH}f01922 P{XP}d02813 /+. This recombination deletes the RpL28 and RpL18 genes; (L) y w eyF; PBac{WH}f01922 P{XP}d07256 /+. This recombination deletes the RpL28, RpL18, and RpL14 genes; Note the small eye size. (M) y w eyF; PBac{WH}f05041 P{XP}d02570 /+; (N) y w eyF; PBac{WH}f05041 P{XP}d02813 /+. This recombination deletes the RpL18 gene; (O) y w eyF; PBac{WH}f05041 P{XP}d07256 /+. This recombination deletes the RpL18 and RpL14 genes; (P) y w eyF; P{XP}d06796 PBac{WH}f04937 /+. This recombination deletes the eIF2γ gene. (Q) y w eyF; P{XP}d06796 PBac{WH}f00971 /+. This recombination deletes the eIF2γ gene. Note the particularly small size of the recombinant heads, which also retain an unusual amount of unrecombined cells; (R) y w eyF; P{XP}d06796 PBac{WH}f03502 /+. This recombination deletes the eIF2γ, Xrp1, RpS20 and RpS30 genes. (S) y w eyF; P{XP}d06928 PBac{WH}f03502 /+. This recombination deletes the Xrp1, RpS20 and RpS30 genes. (T) y w eyF; P{XP}d06928 PBac{WH}f01700 /+. This recombination deletes the Xrp1, RpS20, and RpS30 genes. (U) y w eyF; PBac{WH}f04180 P{XP}d07944 /+. The whole eye resembles the parental genotype lacking eyFlp; (V) y w eyF; P{XP}d06796 PBac{RB}e03186 /+. The whole eye resembles the parental genotype lacking eyFlp; (W) y w eyF; P{XP}d06796 PBac{RB}e03144 /+. The whole eye resembles the parental genotype lacking eyFlp. (X) y w eyF; P{XP}d08241 PBac{RB}e02272 /+. The eye has a mottled appearance indicative of small recombinant clones generated late in development; (Y) y w eyF; P{XP}d08241 PBac{RB}e03937 /+. The eye has a mottled appearance indicative of small recombinant clones generated late in development; (Z) y w eyF; P{XP}d06928 PBac{RB}e03144 /+. The eye has a mottled appearance indicative of small recombinant clones generated late in development.