Figure 3.
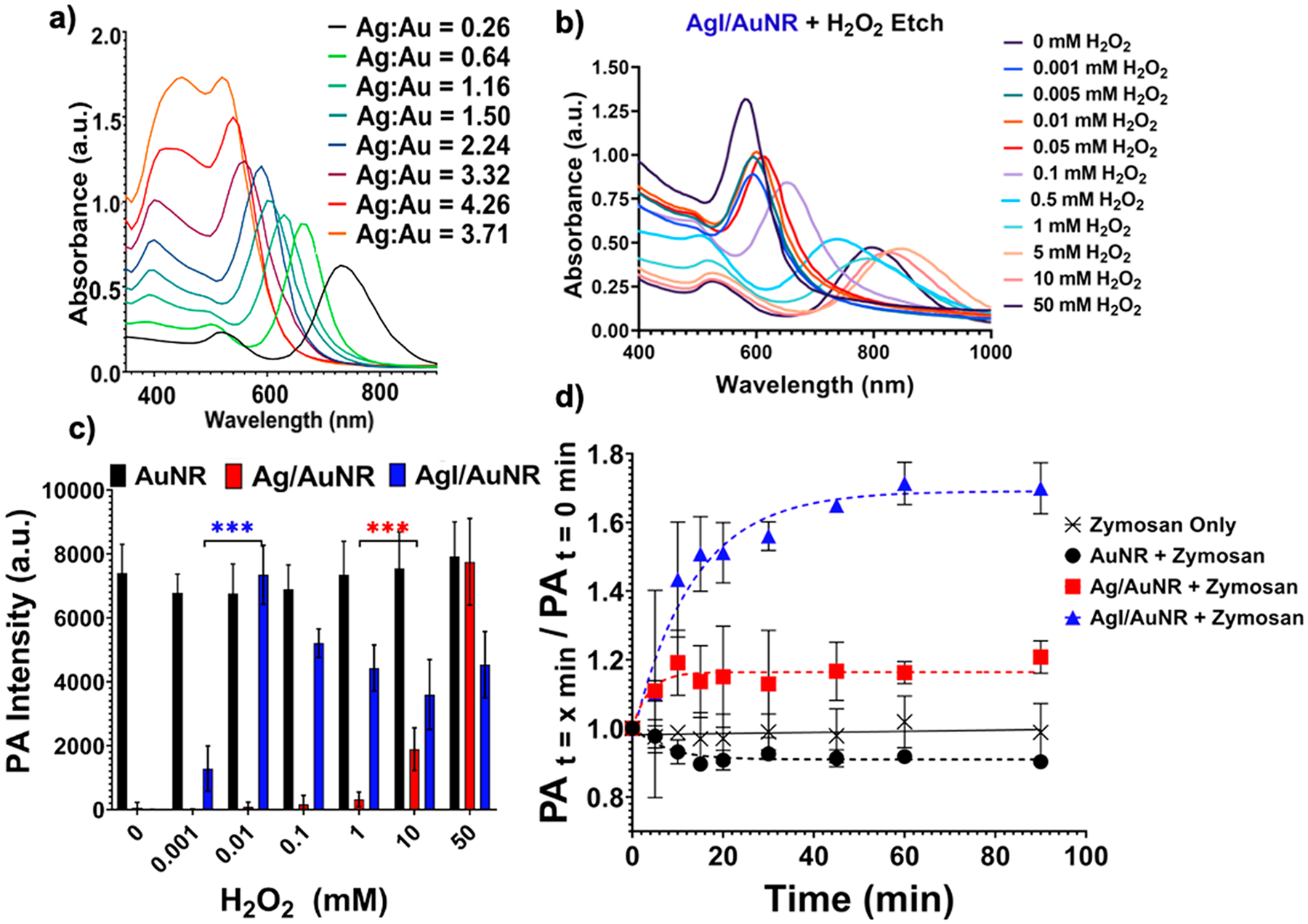
Spectral shifts affect the absorption coefficient. (a) Absorption spectra of silver-coated AuNRs with increasing shell thickness (right to left). Increasing shell thickness causes a blue-shift in the absorption spectra due to a reduction in the AuNR aspect ratio. The μa at 680 nm reduces because of the blue-shift. (b) Selective etching of the silver shell with an increasing concentration of reactive oxygen species (H2O2) restores the AuNR absorption and μa at 680 nm. (c) PA intensity at 680 nm increases as a function of H2O2 concentration as μa increases in (b). (d) In vivo detection of oxidative stress as a function of time. Iodide-doped silver-coated particles are more sensitive to oxidative stress and show a 70% increase in PA intensity over 90 min (680 nm). Adapted with permission from ref 13. Copyright 2020 The Royal Society of Chemistry.
