Fig. 1.
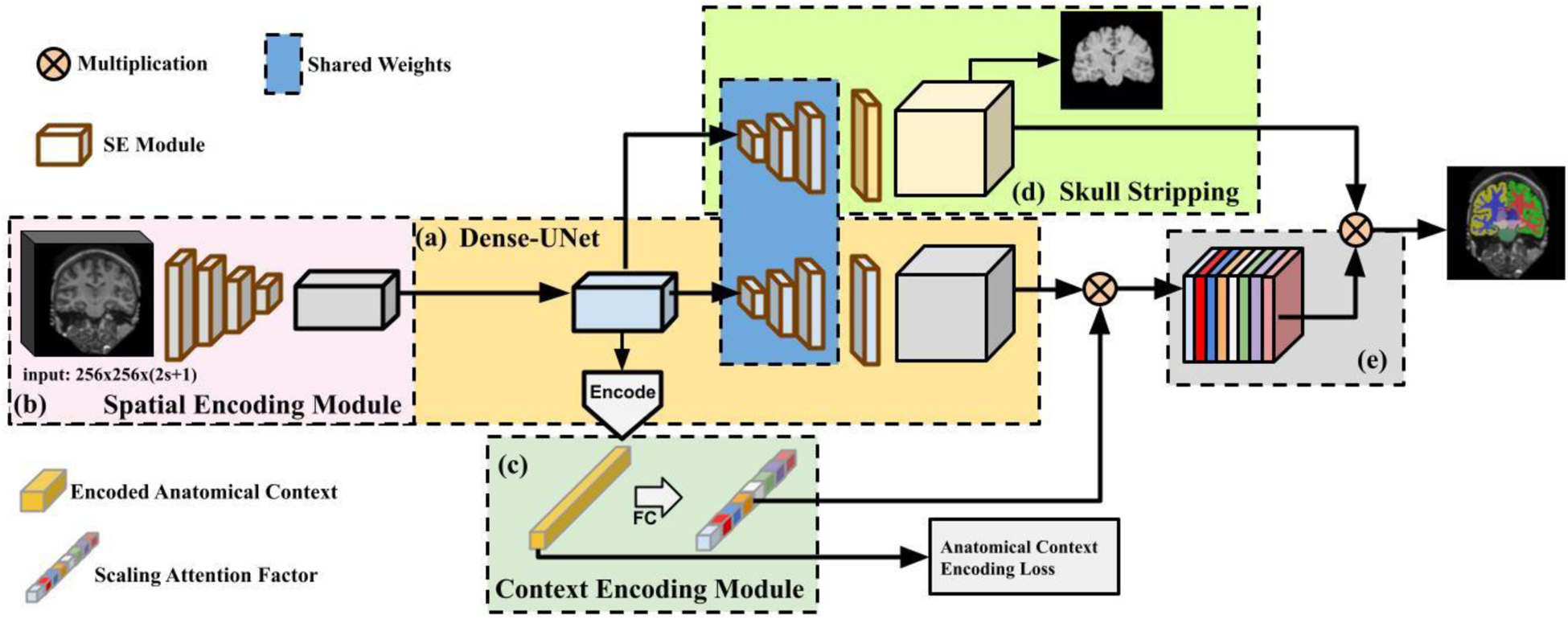
A schematic flowchart of Anatomy Context-Encoding network. (a) A Dense-UNet backbone. (b) A Spatial Context Encoding Module with a 3D image volume as its input. (c) An Anatomical Context Encoding Module contains a context encoder to capture anatomical context. (d) A Skull Striping Module to enforce the network to specifically focus on the brain. Particularly, the spatial encoding module captures 3D features from the input using 2D CNNs. The context encoder captures anatomical context to highlight brain structure-dependent variation by optimizing an Anatomical Context Encoding Loss. The spatial and anatomical semantics (e) and skull stripping features (d) are fused by an element-wise multiplication operation to generate accurate brain structure segmentation result.
