Figure 4. Structural associations with emotion recognition and the metacognitive index.
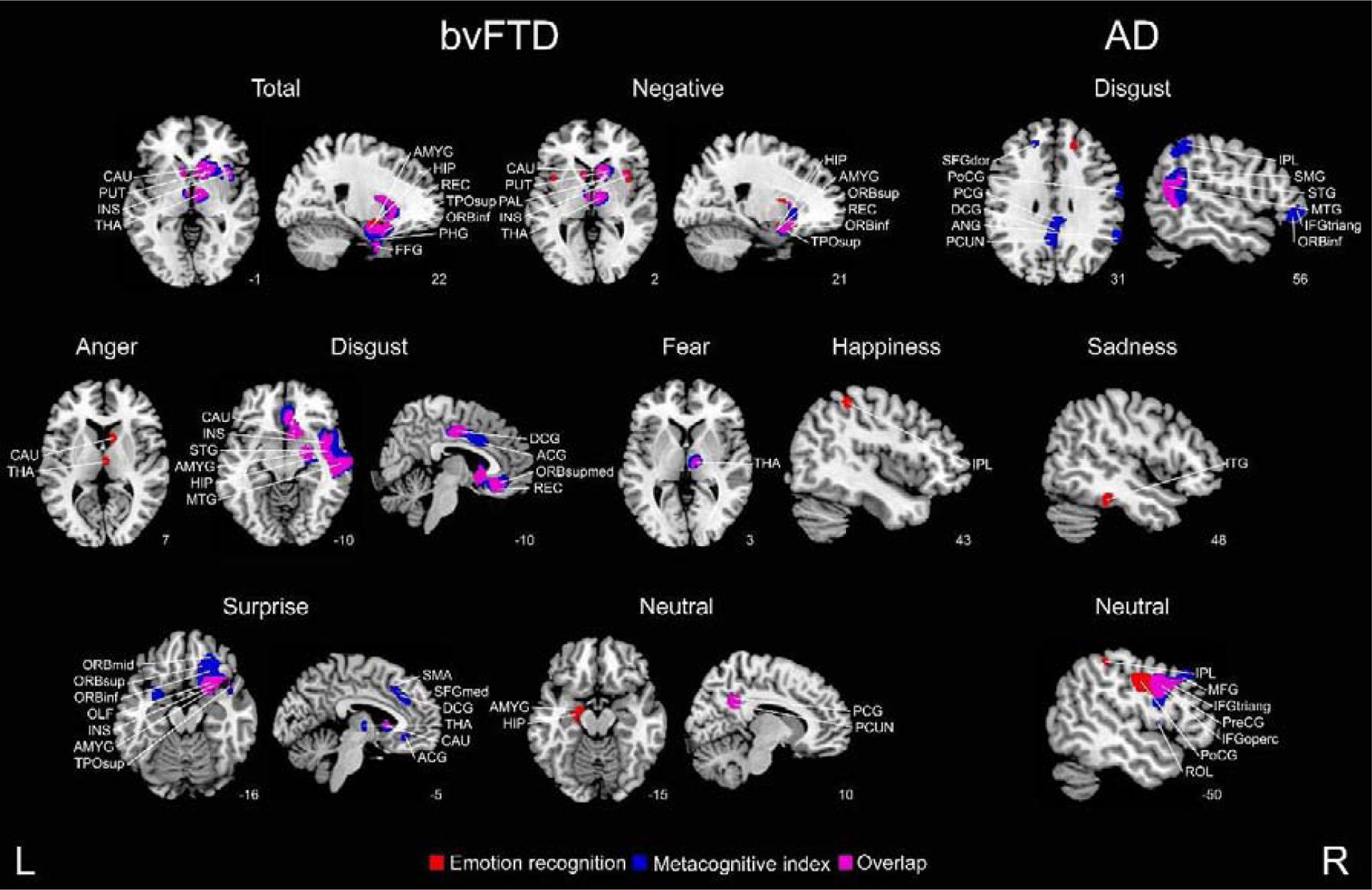
Regression analyses considering bvFTD-controls and AD-controls were conducted to identify regions specific to each patient group and emotion (p < 0 .001, extent threshold = 50 voxels). ACG = anterior cingulate gyrus; AMYG = amygdala; ANG = angular gyrus; CAU = caudate nucleus; DCG = dorsal cingulate gyrus; FFG = fusiform gyrus; HIP = hippocampus; IFGoperc = inferior frontal gyrus (pars opercularis); INS = insula; IPL = inferior parietal gyrus; ITG = inferior temporal gyrus; MFG = middle frontal gyrus; OLF = olfactory cortex; ORBinf = inferior frontal gyrus; ORBmid = middle frontal gyrus; ORBsup = superior frontal gyrus; ORBsupmed = orbitofrontal gyrus; PAL = pallidum; PCG = posterior cingulate gyrus; PCUN = precuneus; PHG = parahipocampal gyrus; PoCG = postcentral gyrus; PreCG = precentral gyrus; PUT = putamen; REC = gyrus rectus; ROL = Rolandic operculum; SFGdor = dorsolateral superior frontal gyrus; SFGmed = medial superior frontal gyrus; SMA = supplementary motor area; SMG = supramarginal gyrus; STG = superior temporal gyrus; THA = thalamus; TPOsup = superior temporal pole; L = left, R = right.
