Extended Data Fig. 5 |. Most genetic variants have little effect on inferred selection at other sites, but a small minority have strong effects.
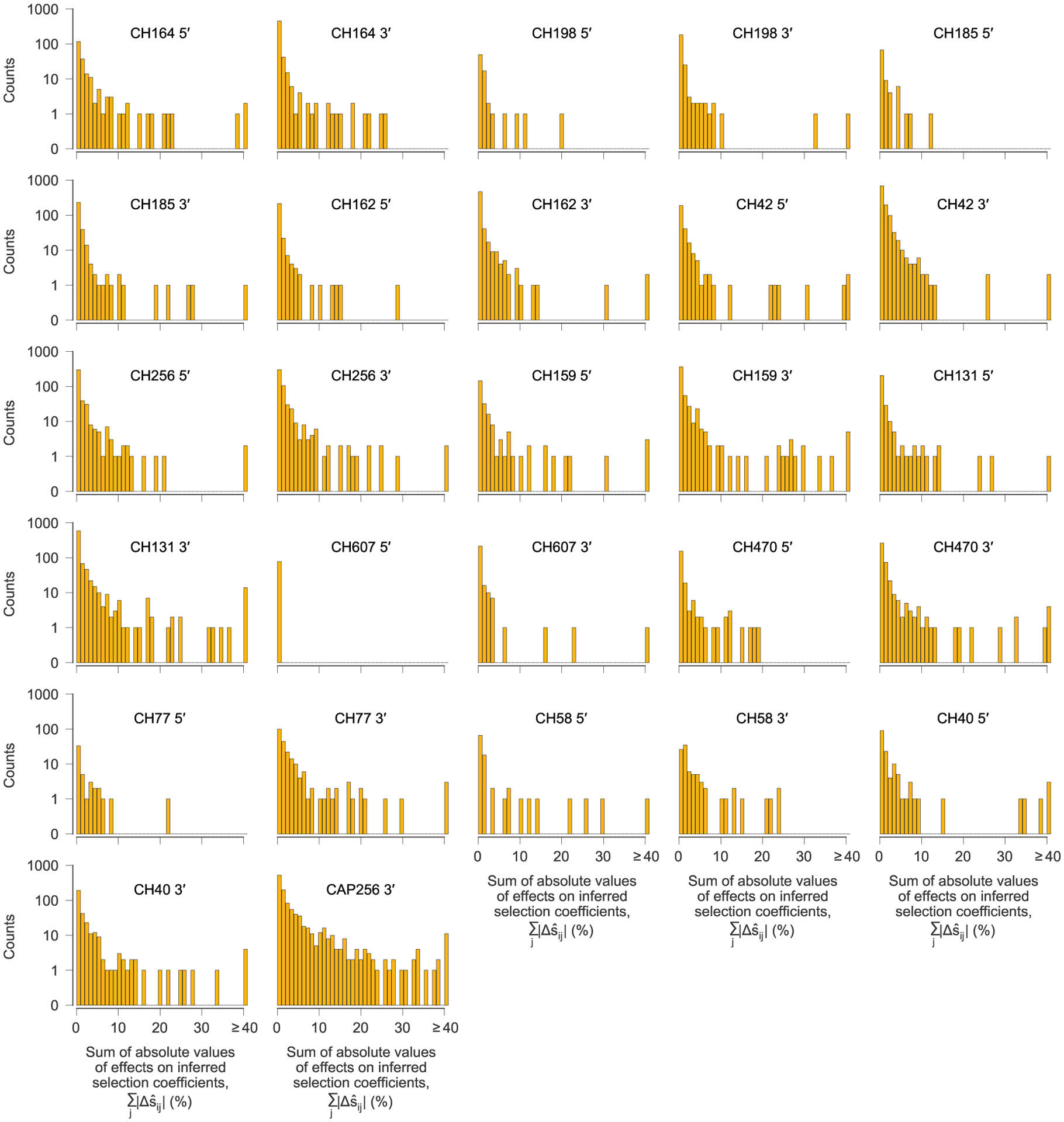
After computing the pairwise effects of each variant i on the inferred selection coefficient for each other variant j, referred to as the target, we summed the absolute value of the values over all target variants j to quantify the influence of each variant i on selection at other sites. One histogram is shown for each sequencing region, for each individual. For the vast majority of variants, the total effect on selection at other sites is near zero. However, a small minority have strong effects. We defined a variant to be ‘highly influential’ if the sum of the absolute values of the over all targets j was larger than 0.4 (=40%).
