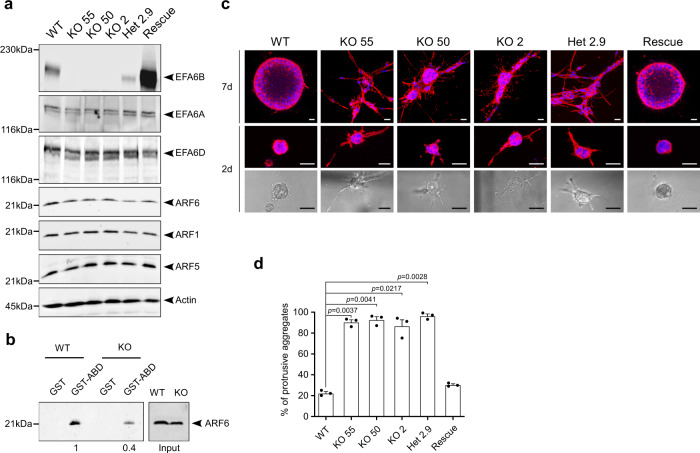
Fig. 1. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knock-out of the EFA6B encoding gene PSD4 in MCF10A cells induces collective invasion in collagen I.
a The MCF10A WT, the homozygous EFA6B KO55, KO50, KO2, the heterozygous EFA6B KO2.9 (Het 2.9) and the EFA6B KO55 over-expressing EFA6B-vsvg cells were solubilized and the expression of the indicated proteins was analyzed by immunoblot. Actin served as a loading control. b Lysates of MCF10A WT and EFA6B KO55 cells were reacted with GST or GST-ABD (ARF6GTP-binding domain of ARHGAP10) bound to glutathione-sepharose beads. The whole lysates and bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-ARF6 antibody. N = 3. c Representative images of the indicated cell aggregates placed in collagen for 7 days (upper panels) or 2 days (middle and bottom panels). The cells were processed for immunofluorescence to label the endogenous F-actin (red) and the nuclei (blue). The bottom panels are bright-field phase-contrast images of the corresponding immunofluorescence images shown in the middle panels. Scale bars 20 μm. d Quantification of the percentage of cell aggregates (n = 100) with invasive protrusions of the indicated MCF10A cell lines grown in collagen for 2 days. N = 3, average ± SEM, one-way ANOVA test with Dunnett’s multiple comparison p-values. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.