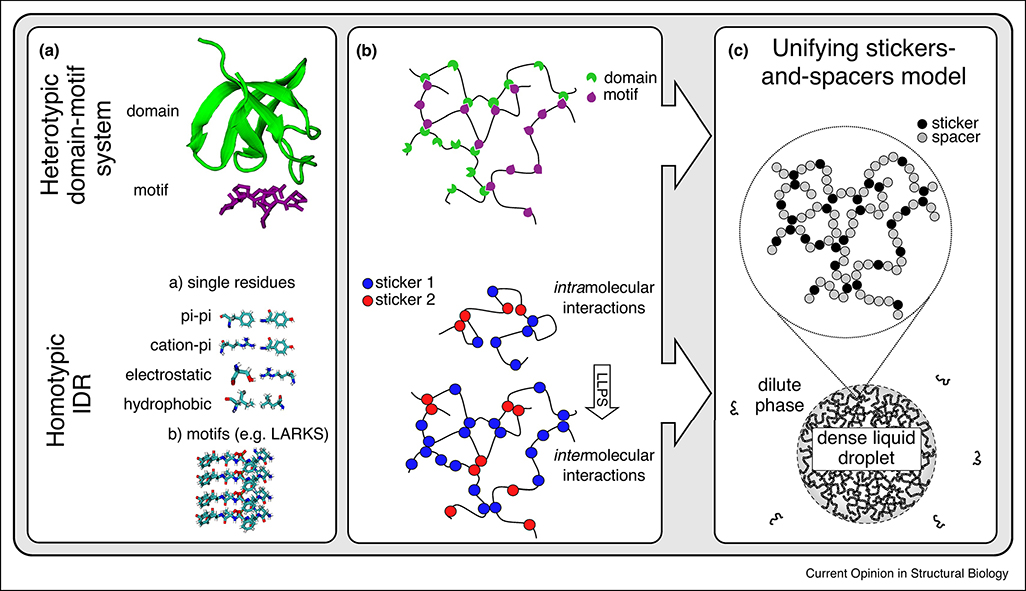
Figure 1. Conceptualizing liquid-liquid phase separation of IDRs.
The interactions that drive LLPS in domain-motif systems and IDRs can both be described by the stickers-and-spacers framework. Stickers are adhesive elements that contribute to the main interaction potential, and they are connected by largely non-interacting spacers. (A) Heterotypic LLPS in domain-motif systems, e.g., between a folded SH3 domain and a proline-rich motif (PRM) (top, PDB ID: 1SEM). LLPS of IDRs can be mediated by a multitude of multivalent interactions. These may include interactions of individual residues or longer motifs, e.g., LARKS (bottom, PDB ID: 6CF4). (B) SH3 tandem repeats connected by linker regions can phase separate in the presence of tandem repeats of PRMs (top). The homotypic intermolecular interactions that drive phase separation of IDRs are satisfied intramolecularly in the dilute phase (bottom). (C) In the stickers-and-spacers framework, SH3 domains and PRMs are stickers, and the connecting linkers are spacers. For IDRs, the single residues or motifs are the stickers and the intervening residues spacers.