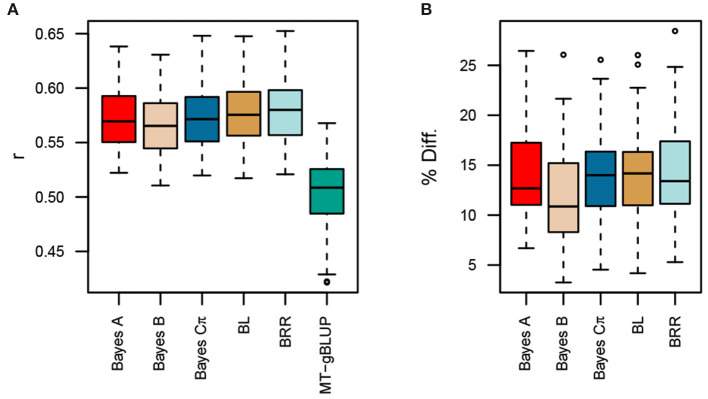
Figure 4.
Comparison of prediction accuracies for multi-kernel trait-specific BLUP models (MK-TGRM-BLUP) and a multi-trait gBLUP approach (MT-gBLUP). The multi-trait gBLUP model used phenotypes for the nine fatty acid traits and total lipid content measured via near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) to predict total lipid content. Prediction accuracy was assessed using five-fold cross validation with 50 resampling runs. Since there is a small overlap between lines in the diversity panel, which have fatty acid phenotypes, and lines in the Elite Panel, these common lines were always included in the training set. The testing set is then 20% of the lines that only have NIRS phenotypes. The correlation between predicted genomic breeding values in the testing population and the average of observed phenotypes across locations is shown in (A). Panel (B) shows the percent improvement relative to MT-gBLUP for each MK-TGRM-BLUP approach. BL, Bayesian LASSO; BRR, Bayesian ridge regression; r, Pearson's correlation coefficient.