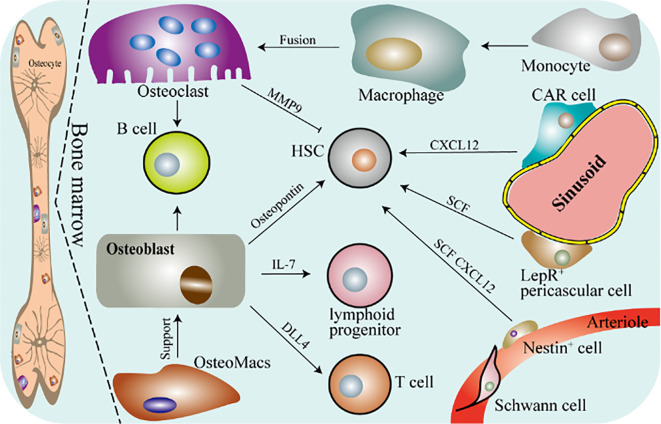
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of osteoimmunity. DLL4, delta-like protein 4; CAR, CXC chemokine ligand (CXCL) 12-abundant reticular; SCF, stem cell factor; HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; LepR, leptin receptor-expressing. Bone marrow mainly contains osteocytes, osteoblasts, osteoclasts, OsteoMacs and macrophages. OsteoMacs refers to the macrophages residing in the bone marrow, accounting for 15% to 20% of the total bone marrow cells. And they are mainly located near osteoblasts and support the generation of osteoblasts and bone formation. Macrophages are differentiated from monocytes derived from peripheral blood and further form osteoclasts. Bone is the cradle of immune cells, osteoclasts and osteoblasts are involved in regulating the immune response of a variety of immune cells. And they can also regulate the function of hematopoietic stem cells.