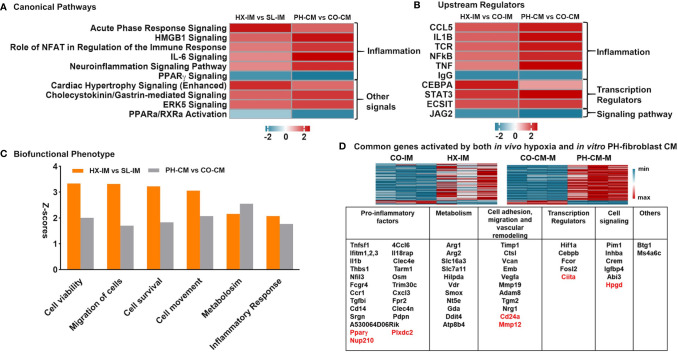
Figure 5.
In vivo lung interstitial/perivascular macrophages isolated from hypoxic mice and in vitro macrophages treated with PH-fibroblast conditioned media share pro-inflammatory and pro-remodeling gene profiles. RNA-seq data of in vitro PH-CM treated vs. CO-CM treated BMDMs and in vivo lung interstitial/perivascular macrophages flow sorted from mouse exposed to 4-day hypoxia (HX-IM) vs. sea level (CO-IM) were analyzed. The cutoff criteria is q ≤ 0.05 and FC ≥ |2| in order to match the differing data set sizes and to limit our findings to only the most biologically significant pathways. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis identified similarities in: (A) Canonical pathways, (B) Upstream regulators, and (C) Biofunctional phenotypes, part of Disease and Biofunctional profile analysis, with z-score ≥ |2.0| in at least one dataset and p-values of overlap ≤ 0.05 in both data sets. (D) Common genes significantly regulated by both in vivo hypoxia and in vitro PH-CM. Genes were clustered in five key categories by their functions: pro-inflammation, metabolism, cell adhesion/migration/vascular remodeling, transcription regulators, and cell signaling. Down-regulated genes are highlighted in red.