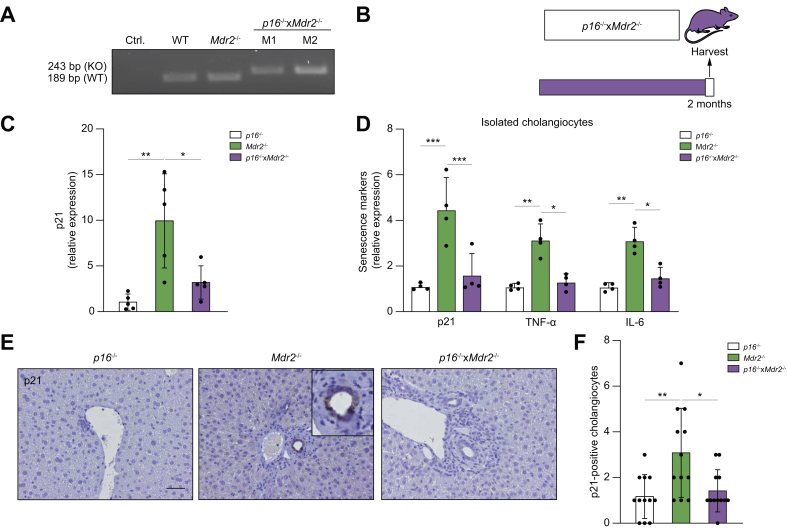
Fig. 3.
Genetic reduction of p16 reduces senescence markers in the Mdr2-/- mouse.
(A) PCR genotyping showing the p16-/- DNA construct. (KO) band represents the neomycin-resistance cassette on exon-1α of the Ink4a/Arf/Ink4b locus. (B) Schematic of the experimental design. P16-/-, Mdr2-/-, and crossbred p16-/-xMdr2-/- mice were harvested at 2 months of age. (C) Hepatic p21 mRNA expression, as assessed by RT-PCR, was reduced in p16-/-xMdr2-/- mice. (D) mRNA expression of senescence markers in isolated cholangiocytes, as assessed by RT-PCR, was reduced in p16-/-xMdr2-/- mice. (E) Representative images of p21 immunohistochemistry of p16-/- (left), Mdr2-/- (middle), and p16-/-xMdr2-/- mice (right) (magnification: 20×). A significant reduction in the number of p21-positive cholangiocytes was observed in p16-/-xMdr2-/- mice compared with the control group. (F) Quantification of p21-positive cholangiocytes. Each dot represents an image with at least 1 bile duct. Bars represent mean ± SD; n = 5–7. Scale bar: 50 μm (D). ∗p <0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, (Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). Mdr2, multidrug-resistance 2; RT, reverse transcription; TNF, tumour necrosis factor; WT, wild-type.