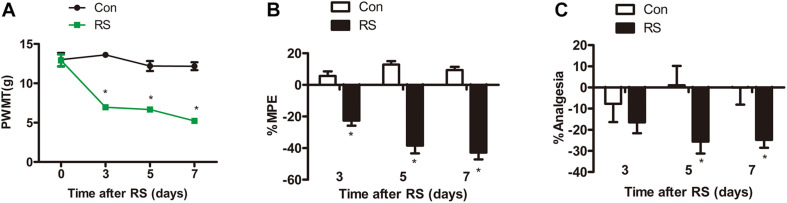
FIGURE 1.
Mechanical or thermal nociceptive thresholds in rats with or without chronic RS. (A–C) Nociceptive behavior tests including PWMT (RS effect: F1,22 = 192.322, P < 0.001; observation intervals: F3,66 = 22.641, P < 0.001; interaction: F3,66 = 16.798, P < 0.001), PWTL (RS effect: F1,22 = 141.084, P < 0.001; observation intervals: F2,44 = 4.606, P = 0.015; interaction: F2,44 = 12.632, P < 0.001), and TFL (RS effect: F1,22 = 5.457, P = 0.029; observation intervals: F2,44 = 0.002, P = 0.998; interaction: F2,44 = 2.552, P = 0.089). Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 12). *Significant difference with respect to control groups (two-way ANOVA with repeated measures in nociceptive behavior tests, followed by Bonferroni post hoc test or Dunnett’s T3 test if necessary). *P < 0.05. RS, restraint stress; PWMT, paw withdrawal mechanical threshold; PWTL, paw withdrawal thermal latency; TFL, tail-flick latency; NO, nitric oxide; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase.