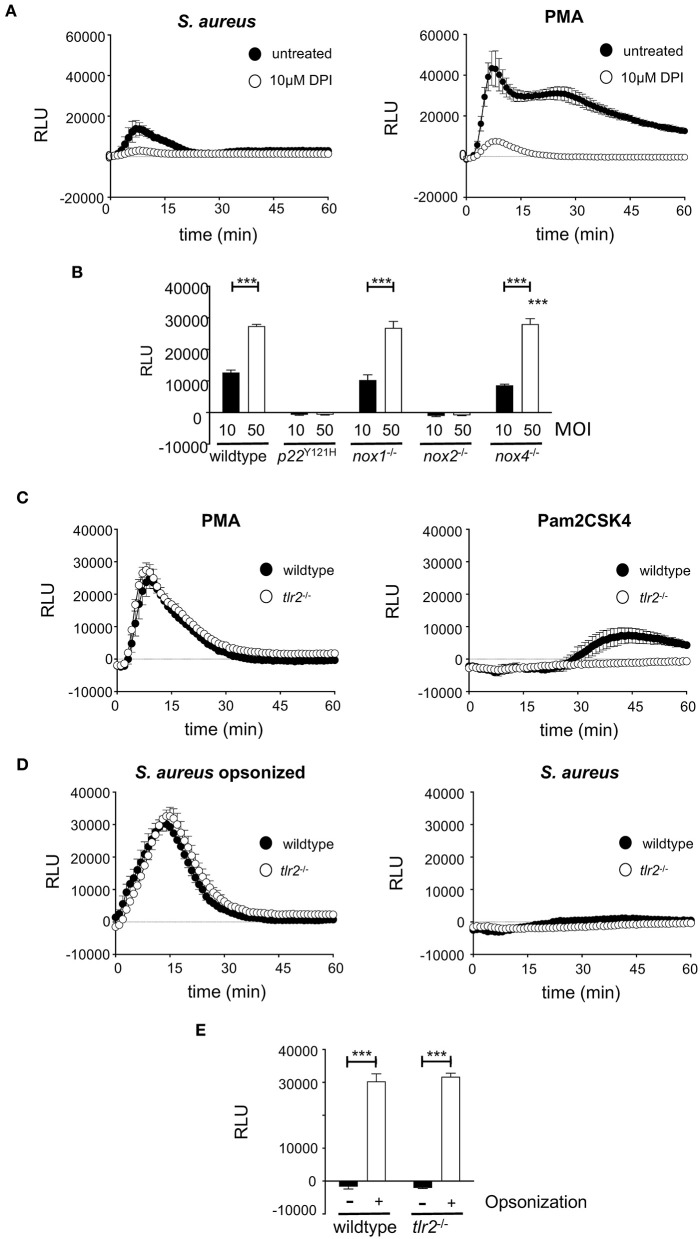
Figure 1.
Opsonophagocytosis of S. aureus leads to NOX2 dependent ROS production in macrophages. For ROS measurement, 1 × 105 wildtype or knockout BMDM were seeded in a white 96-well plate without antibiotics 16 h prior to measurement. ROS production was measured using Luminol in a Luminometer preheated to 37°C. (A) ROS production in wildtype BMDM incubated with opsonized S. aureus (MOI50; left) or 10μM PMA (right) in the absence (closed circles) or presence of 10 μM DPI. (B) Peak value of ROS production at 13 min after infection with opsonized S. aureus MOI10 (closed bars) or MOI50 (open bars) in wildtype and NADPH-oxidase deficient BMDMs. Shown are mean and SD of triplicates corrected for non-infected control of a representative experiment performed at least three times. Statistical significance was analyzed by unpaired two-sided Student's t-test using GraphPad Prism 5.01 between indicated conditions (***=p < 0.001). (C) ROS production in wildtype (closed circles) or tlr2−/− BMDM (open circles) stimulated with 10 μM PMA (left), or 100 ng/ml Pam2CSK4 (right). (D) ROS production in wildtype (closed circles) or tlr2−/− BMDM (open circles) upon infection with S. aureus MW2 opsonized with 5% mouse serum (MOI50; left) or non opsonized S. aureus (MOI50; right). (E) Peak value of ROS production at 13 min after infection with non-opsonized (closed bars) or opsonized S. aureus (open bars) in wildtype and tlr2−/− BMDM. Shown are means and SD of triplicates of a representative experiment performed at least three times. Statistical significance was analyzed by unpaired two-sided Student's t-test using GraphPad Prism 5.01 between indicated conditions (***=p < 0.001). NOX, NADPH Oxidas; ROS, reactive oxygen species; PMA, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate; DPI, diphenyleniodonium; MOI, multiplicity of infection; BMDMs, bone marrow derived macrophages; SD, standard deviation; TLR2, Toll-like receptor 2; NMS, normal mouse serum; p.i., post infection; CFU, colony forming unit; i.v., intravenous; s.c., subcutaneous.