Fig. 9.
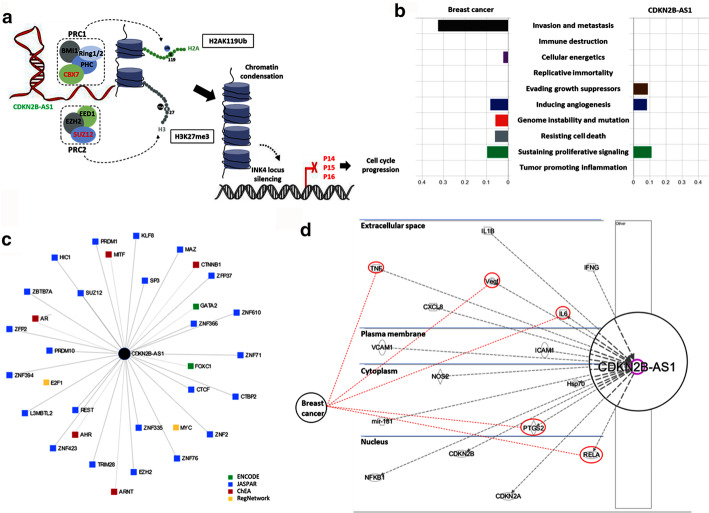
Functional role of CDKN2B in cancer. a In cis and in trans gene regulation of CDKN2B-AS1 through chromatin modification complexes. CDKN2B-AS1 acts as docking for the epigenetic regulators, PRC1 and PRC2 polycomb complexes, to modify the histone code. The PRC1 complex includes multiple subunits, such as PHC, CBX7, BMI1, and RING1a/1b, which are implicated in the maintenance of silencing by catalyzing monoubiquitination of histone H2A (H2AK119ub1). The PRC2 complex comprises the JARID2, EED, SUZ12, and EZH2 subunits which maintain chromatin repression by catalyzing mono-/di-/trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27me1, H3K27me2, and H3K27me3). b Automatic CHAT classification of the PubMed literature according to the hallmark of cancer taxonomy. Breast cancer and CDKN2B-AS1 (data are shown as NPMI; normalized pointwise mutual information) were compared. Each bar demonstrates cancer hallmark and/or biological process association with the search query. c Transcription factors-gene network in Network Analyst. A total of 34 nodes representing TF-gene interactions with the lncRNA CDKN2B-AS1 and edges with length representing the degree of association score. Different databases were used: ENCODE, JASPAR, ChEA, and RegNetwork. d Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. A gene network was built to connect key genes highly enriched with the lncRNA. The direction of activity (activation/inhibition) is shown. Five molecular targets involved in breast cancer are further connected in red