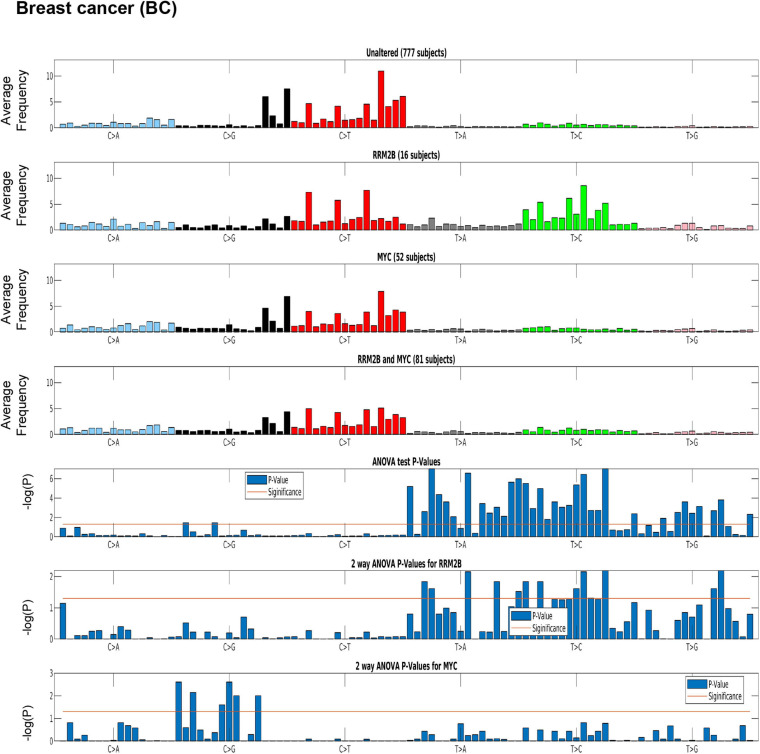
FIGURE 5.
Mutation signature in breast cancer (BC) cases segregated by amplification type. One-way ANOVA (RRM2B amplifications only vs. other groups) and two-way ANOVA (included group with RRM2B and MYC co-amplifications) analysis showed that the T > C and T > G mutations are statistically significant. Top panels: tumor whole-exome sequence data from the PanCancer Atlas studies was used to calculate the average frequency of the 96 trinucleotide context mutations in each group: unaltered cases, cases with only RRM2B amplifications, cases with only MYC amplifications, and cases with amplifications in both. Bottom panels: The statistical significance of each comparisons is represented by ANOVA tests as -log10 (P-value) for each of the 96 trinucleotide context mutations. The -log10 (P) visualizations are provided for: one-way ANOVA comparing RRM2B only group to all other groups, a two-way ANOVA comparing all groups with RRM2B or MYC amplifications. -log10 (P)—the taller the bars are, the lower is the P-value and when the bars exceed the red line, P-values are less than 5%. P-values of each subfigure have been corrected using Benjamini–Hochberg procedure.