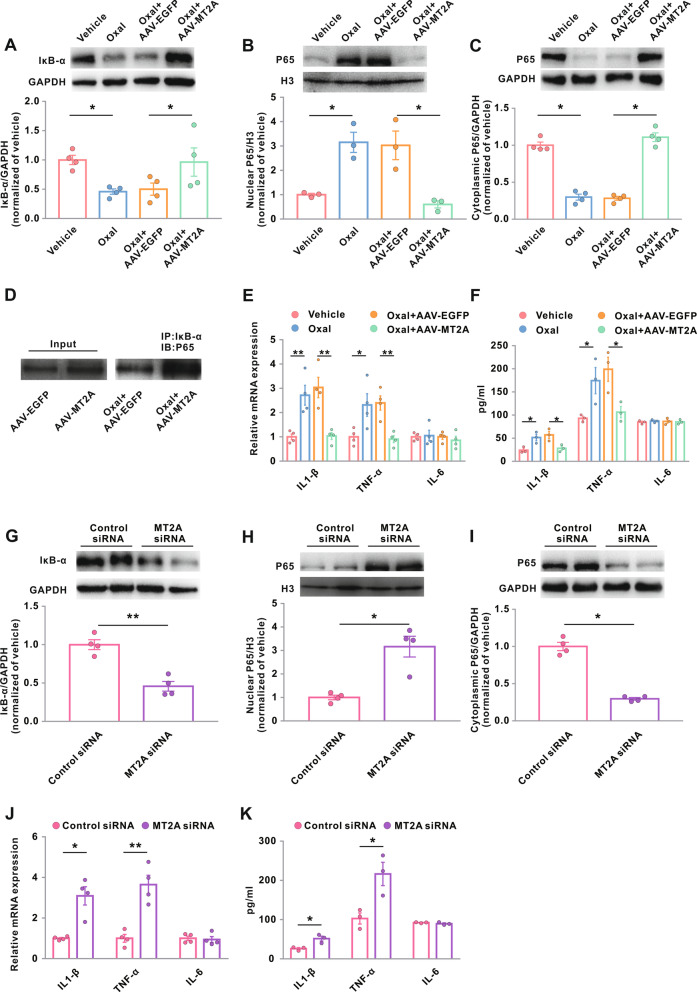
Fig. 5.
MT2 inhibits oxaliplatin-induced activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in the spinal dorsal horn. a–f Rats were treated with vehicle or Oxal (0.4 mg/100 g/day for five consecutive days) 21 days after intraspinal injection of AAV-MT2A-EGFP or AAV-EGFP. g–k Naive rats were treated with intrathecal injection of MT2A or control siRNA. Then, the L4–L6 dorsal horns were harvested for the following examines. a, g Protein levels of IκB-α. GAPDH served as loading controls. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01; n = 4. Protein levels of NF-κB P65 in the nucleus (b, h) and in the cytoplasm (c, i). H3 and GAPDH served as loading controls for nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins, respectively. *p < 0.05; n = 4. d IP with IκB-α antibody followed by immunoblotting using P65 antibody. e, j Transcriptional levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01; n = 4. f, k Translational levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 in ELISA. *p < 0.05; n = 3. Oxal, oxaliplatin