Figure 1.
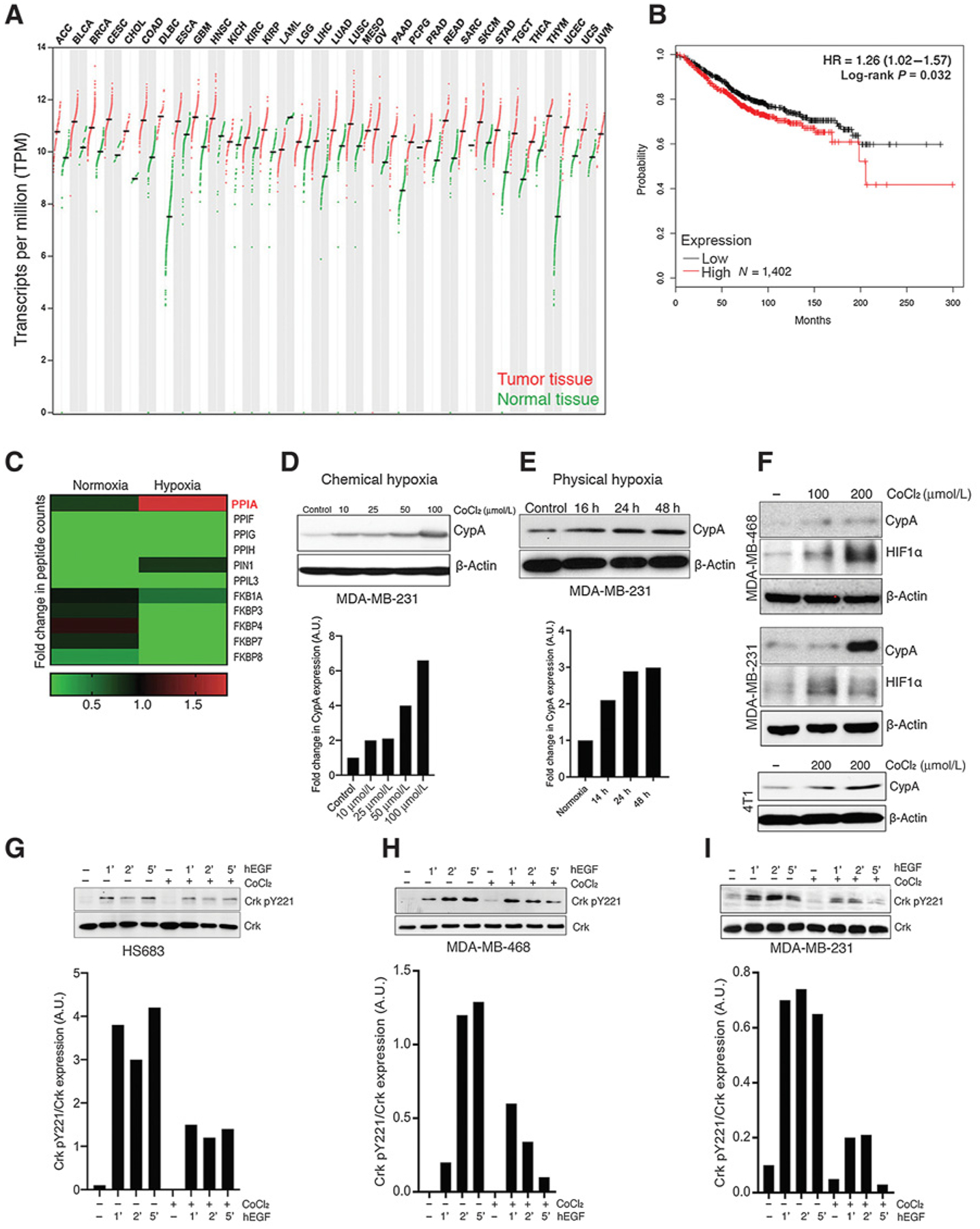
Hypoxia induces CypA expression and suppresses EGF-induced Crk Y221 phosphorylation. A, Expression of CypA in human cancers by TCGA RNA-seq data analysis. Log2 (TPM+1) scale of transcript per million of CypA in indicated number of normal and cancerous tissues are shown. B, Distant metastasis–free survival of breast cancer tumor RNA-seq data analyzed by CypA expression [high (red; N = 1035) and low (black; N = 711) expression] and presented in Kaplan–Meier curve. HR and P value calculated using Cox regression analysis are indicated. C, Protein expression of multiple proline-prolyl isomerase upon induction of hypoxia by mass spectrometric analysis. Relative change in peptide counts of each proline-prolyl isomerase in normoxic and hypoxic conditions presented in heatmap. D and E, Western blot analysis of CypA gene expression in MDA-MB-231 by chemical hypoxia (CoCl2 treatment; a) and physical hypoxia (hypoxia chamber; b). F, Western blotting analysis of hypoxia-induced CypA and HIF1α expression in MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468, and 4T1 cells. Representative images from Western blot analysis of Crk Y221 phosphorylation upon induction of hypoxia in HS683 (G), MDA-MB-468 (H), and MDA-MB-231 cells (I). Densitometric analysis using ImageJ is shown below each panel. The bar graphs represent mean expression of Y221 phosphorylated versus total Crk in each group from three independent experiments. Cells were pretreated with CoCl2 overnight in serum-starved medium followed by EGF stimulation for indicated time points, lysates were made and probed for Crk Y221 phosphorylation. ACC, adrenocortical carcinoma; BLCA, bladder urothelial carcinoma; BRCA, breast invasive carcinoma; CESC, cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma; CHOL, cholangiocarcinoma; COAD, colon adenocarcinoma; DLBC, lymphoid neoplasm diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; ESCA, esophageal carcinoma; HNSC, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; KICH, kidney chromophobe; KIRC, kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; KIRP, kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma; LAML, acute myeloid leukemia; LGG, brain lower grade glioma; LIHC, liver hepatocellular carcinoma; LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC, lung squamous cell carcinoma; MESO, mesothelioma; OV, ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma; PAAD, pancreatic adenocarcinoma; PCPG, pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma; PRAD, prostate adenocarcinoma; READ, rectum adenocarcinoma; SARC, sarcoma; SKCM, skin cutaneous melanoma; STAD, stomach adenocarcinoma; TGCT, testicular germ cell tumors; THCA, thyroid carcinoma; THYM, thymoma; UCEC, uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma; UCS, uterine carcinosarcoma; and UVM, uveal melanoma.
