Figure 2.
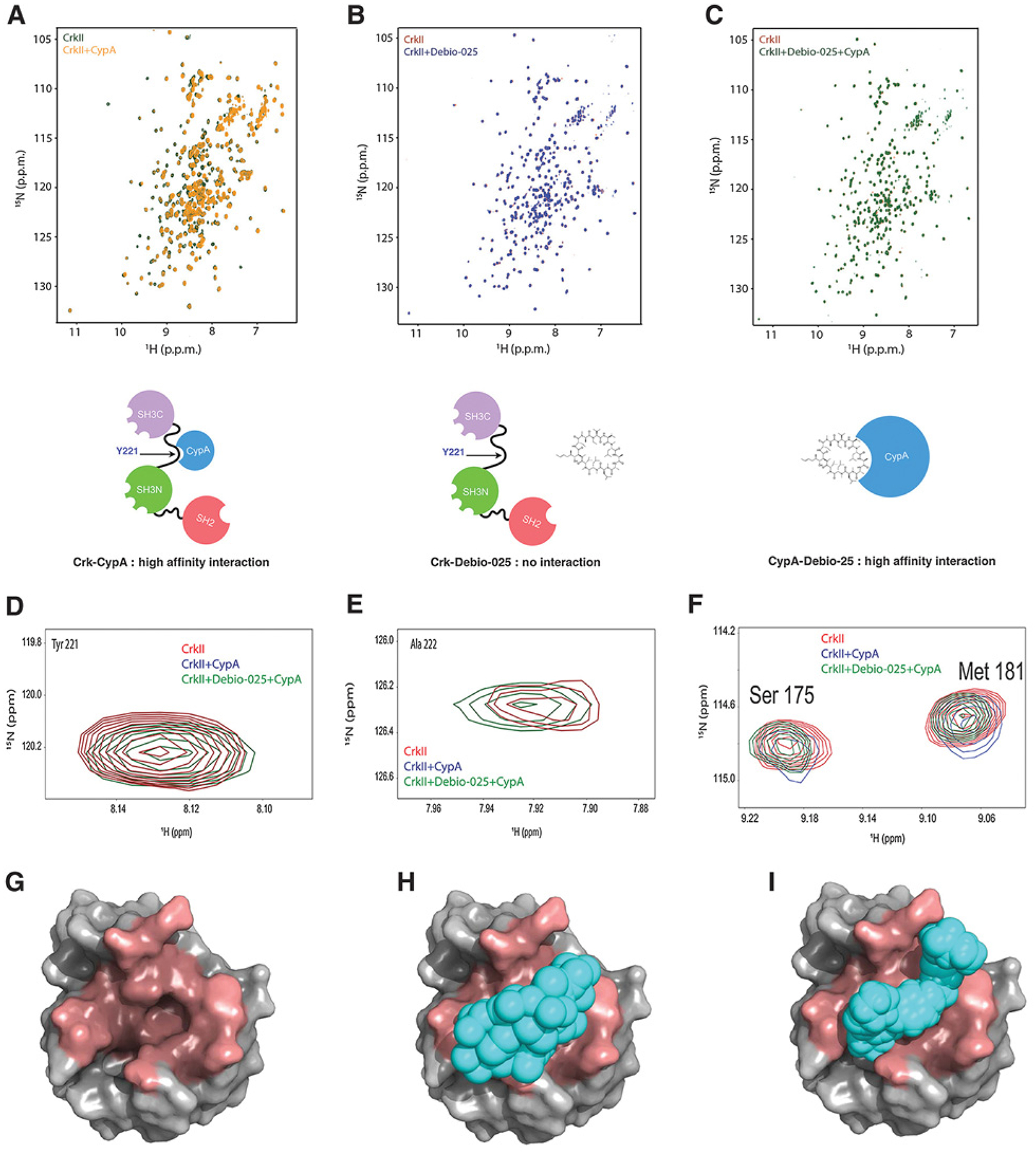
Debio-025 disrupts the Crk–CypA complex formation by a CypA-specific interaction. A, Overlaid 1H-15N Heteronuclear Single Quantum Coherence (HSQC) NMR spectra of labeled CrkII (green) and labeled CrkII titrated with equimolar unlabeled CypA (yellow). B, Overlaid 1H-15N HSQC NMR spectra of labeled CrkII (red) and labeled CrkII titrated with equimolar Debio-025. C, Overlaid 1H-15N NMR spectra of labeled CrkII (red) and labeled CrkII titrated with equimolar unlabeled CypA–Debio-025 complex (green). Schematic models are shown for each condition below. D–F, Zoomed view of 1H-15N HSQC NMR spectra of residues of CrkII showing interaction with CypA. G–I, Molecular models showing CrkII and Debio-025 occupy the same binding site on CypA. CypA (gray, PDB:ID 5HSV) shown as a surface representation and binding pocket for Debio-025 and CrkII (dark red; G), Debio-025 (cyan) bound to CypA (H), and CrkII peptide (216 - PEPGPYAQP - 224; cyan) bound to CypA (PDB ID: 2ms4; I). CrkII and Debio-025 occupies the same binding site on CypA.
