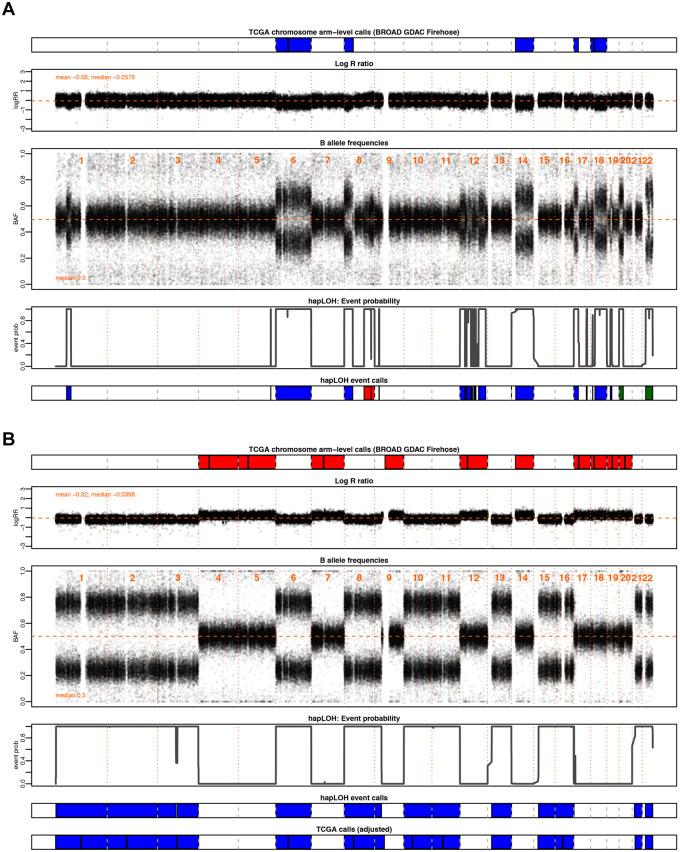
Figure 1.
Examples highlighting the utility of BAF in the identification of chromosomal alterations. Through this investigation, we aim to supplement the SCNAs in TCGA with AI inferred from BAF patterns, a complementary data element to the LRR, from which existing calls are made, to identify additional chromosomal alterations. Shown here are two motivating examples from pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD). The tumor samples are annotated with chromosomal arm-level events downloaded from BROAD GDAC Firehose along with the BAF and LRR values at markers profiled across the genome for that individual. Below these panels are the event probabilities inferred from hapLOH using the BAF patterns, as well as classified event calls from hapLOH using a threshold-based approach from BAF and LRR deviations, for the identified event boundaries (see Materials and methods). Although all hapLOH events are shown, only chromosomal-arm level events were used for the comparison to SCNAs identified in TCGA. The events calls from hapLOH as well as the chromosomal arm-level events reported by TCGA have been colored based on the type of chromosomal alteration (red: gain, blue: loss). (A) A PAAD tumor exhibiting overall concordance between the two call sets, with additional cnLOH events such as those on chromosome 22 and arm 20p, identified by hapLOH. In such cases, our approach of a BAF-derived AI estimator supplements the database with additional, potentially impactful, chromosomal alterations. (B) A PAAD sample with discordant calls between the two approaches. The incorporation of deviations in BAF suggests a misestimation of the normal region. The SCNAs reported in TCGA do not align with BAF deviations. However, hapLOH identifies regions based on BAF-derived AI. We apply an automated adjustment approach (see Materials and methods) for such discordant cases, the result of which is shown in the bottom-most panel. The SCNAs, after adjustment, align with deviations in BAF and thereby are concordant with hapLOH event calls. Through this approach, we address differences between the call sets and suggest methods to adjust specific cases with potentially problematic calls to enhance the database with more accurate SCNAs.