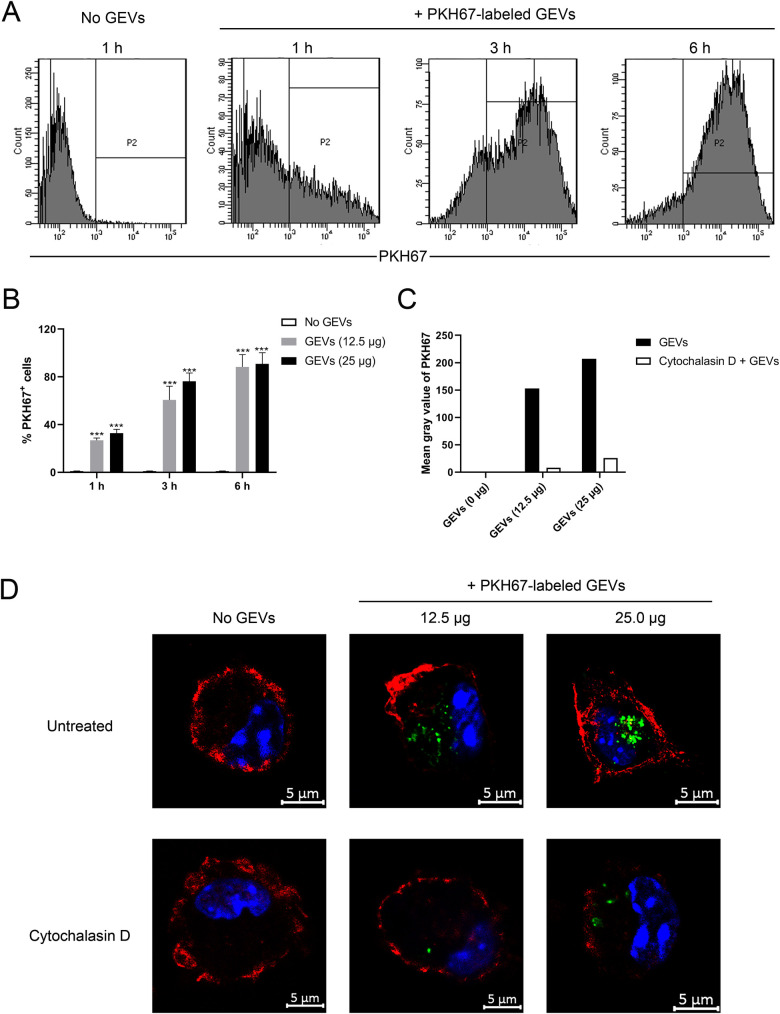
Fig 2. GEVs are actively captured by murine peritoneal macrophages.
(A) Twenty-five microgram of GEVs were inoculated into murine peritoneal macrophages, incubated for time periods of 1, 3 and 6 h, and detected through flow cytometry. (B) Different doses of GEVs (25 μg or 12.5 μg) were inoculated into macrophages, incubated for the indicated time, and detected through flow cytometry. Significance is shown as ***p < 0.001. Three biological replicates were set for each treatment. (C, D) Macrophages were pretreated with 10 μM cytochalasin D for 4 h, inoculated with 12.5 μg or 25 μg of GEVs, and incubated for 6 h. Cells without cytochalasin D pretreatment were used as positive control. Then, cells were stained for confocal microscopy observation: green, PKH67-labeled GEVs; red, host F-actin; blue, nuclei. Scale bars: 5 μm. The mean gray value of PKH67 in GEVs treatment or cytochalasin D combined GEVs treatment groups were calculated using Image J software.