Fig. 1. Overview of the fragment discovery approach for SARS-CoV-2 Nsp3 Mac1 presented in this study.
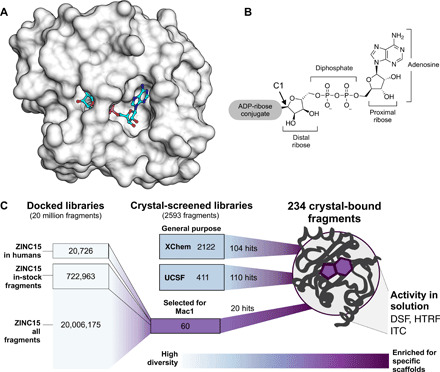
(A) Surface representation of Nsp3 Mac1 with ADPr bound (cyan) in a deep and open binding cleft. (B) Nsp3 Mac1 has (ADP-ribosyl)hydrolase activity, which removes ADP-ribosylation modifications attached to host and pathogen targets. ADPr is conjugated through C1 of the distal ribose. (C) Summary of the fragment discovery campaign presented in this work. Three fragment libraries were screened by crystallography: two general-purpose [XChem and University of California San Francisco (UCSF)] and a third bespoke library of 60 compounds, curated for Mac1 by molecular docking of more than 20 million fragments. Crystallographic studies identified 214 unique fragments binding to Mac1, while the molecular docking effort yielded 20 crystallographically confirmed hits. Several crystallographic and docking fragments were validated by isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF), and a HTRF-based ADPr-peptide displacement assay.
