Figure 5: The lentiviral shRNA-mediated knock-down of BTK expression in primary human lymph node-derived B cells results in strong augmentation of sIG-crosslinking induced AKT phosphorylation.
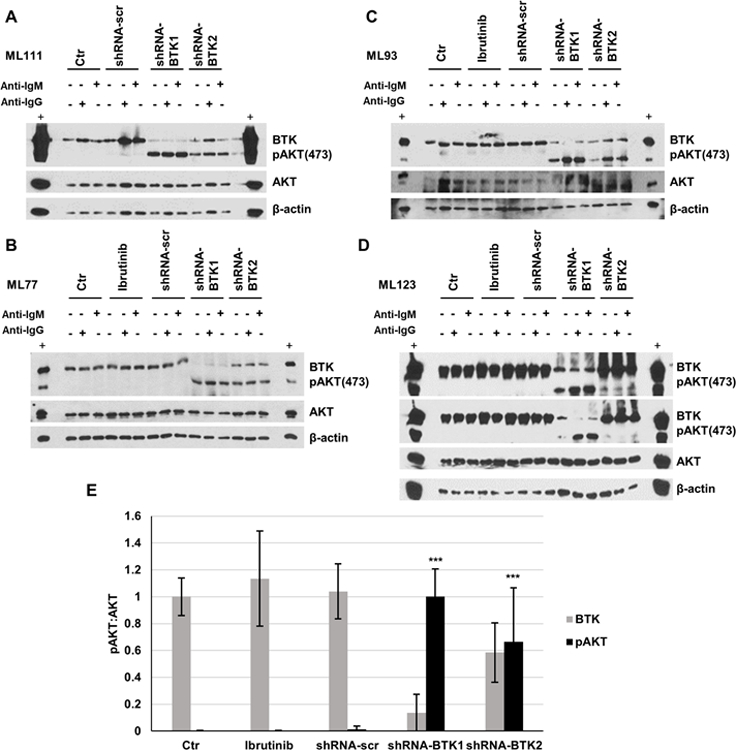
Non-malignant human lymph node derived B cells were purified from LN biopsies via depletion of CD3+ and CD14+ cells. Purified B cells were cultured and transduced using highly concentrated lentiviral preparations of pLKO-BTK targeted or a scrambled shRNA. Following 36 h culture in B cell medium, cells were rested for 1 h in serum-free medium followed by treatment with anti-IG at 10 µg/ml for 10’. Detergent cell lysates were made, fractioned by SDS-PAGE and prepared for immunoblotting with antibodies targeting the indicated epitopes. A–D: Displayed are immunoblotting data based on four separate lymph node biopsies (Ctr: uninfected; shRNA-scr: scrambled shRNA; panel D: long and short pAKT exposures are shown). E: Displayed are composite densitometry data for BTK and p-AKT473:AKT from four experiments shown in A–D. (unpaired t-test; *** p<0.001).
