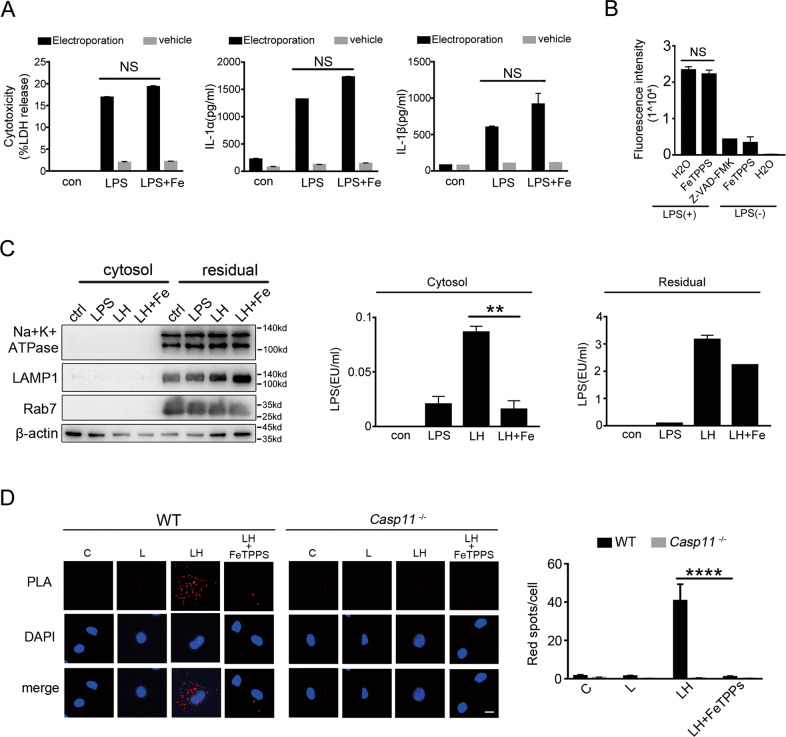
Fig. 4. FeTPPS inhibits HMGB1-mediated cytosolic delivery of LPS.
A LDH and IL-1α, IL-1β release 16 h post-LPS transfection with or without FeTPPS from WT or Casp11−/− peritoneal macrophages. B LPS-induced activation of insect cell-derived caspase-11 in the presence or the absence of FeTPPS or pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD-FMK. H2O was added as control. Caspase activity was determined by measuring the fluorescence intensity of free AMC hydrolyzed from zVAD-AMC. C Western blots for Na+/K+ ATPase, LAMP1, Rab7 (left panel), and LAL assay for LPS (EU, endotoxin units) in the cytosolic and residual fractions of mouse peritoneal macrophages treated with LPS alone (1 μg/mL) or LPS (1 μg/mL) + HMGB1 (400 ng/mL) in the absence or presence of FeTPPS for 2 h. Data presented as mean ± SD of technical replicates. An unpaired t-test (two-sided) was used. **P = 0.0089. D Interaction between caspase-11 and LPS was visualized as red spots under fluorescence microscopy using the proximity-ligation assay (PLA). Mouse peritoneal macrophages stimulated with LPS alone (5 μg/mL) or LPS (5 μg/mL) + HMGB1 (10 μg/mL) (LH) in the absence or presence of FeTPPS (1 μM) for 2 h. Scale bar: 10 μm. Data presented as mean ± SD of technical replicates. An unpaired t-test (two-sided) was used. ****P < 0.0001. Graphs are representative of at least three independent experiments.