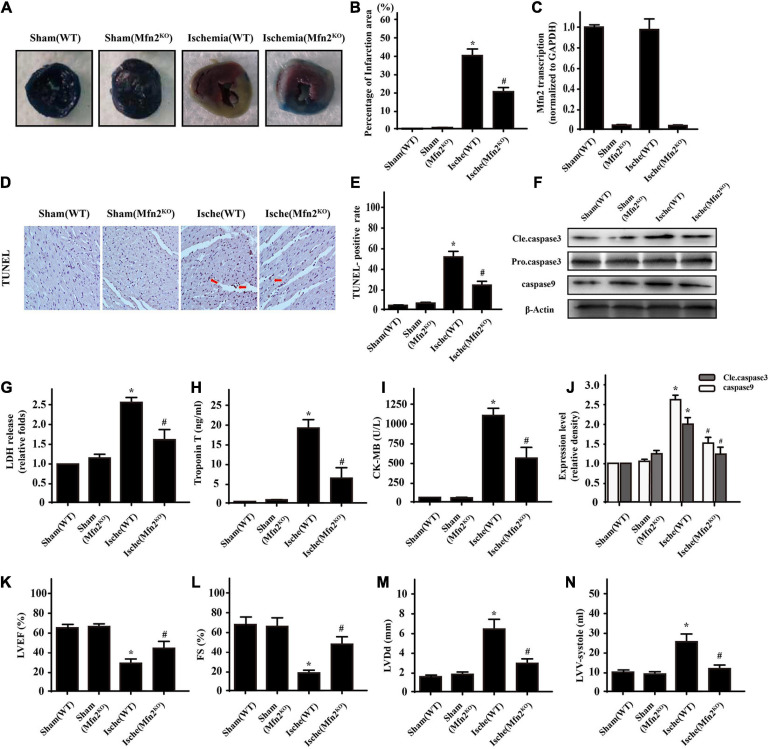
FIGURE 5.
Knockdown of Mfn2 decreased heart infarction under cardiac ischemic injury conditions (n = 3/group). (A,B) Representative images of heart sections with TTC and Evans Blue staining of the infarcted area. The bar graph indicates the infarct size (ischemia group 42.3 ± 4.5% vs. Mfn2KO group 21.9 ± 2.4%, p < 0.05). (C). qPCR was used to test the efficiency of Mfn2 knockout in the Mfn2KO mice. (D,E) The ischemic injury group presented more TUNEL-positive cells than the sham group. (F,J) Western blot analysis was performed to detect apoptosis-related protein expression in different groups. (G–I) ELISA analysis found significantly higher levels of LDH, troponin T, and CK-MB after ischemic injury, while the Mfn2KO group showed some reversal of these effects. (K–N) Representative M-mode echocardiograms were performed after 1 h of heart ischemic injury in each group, and quantitative analysis of the cardiac data derived from echocardiograms was performed. *p < 0.05 compared with the Sham(WT); #p < 0.05 compared with the Ische(WT).