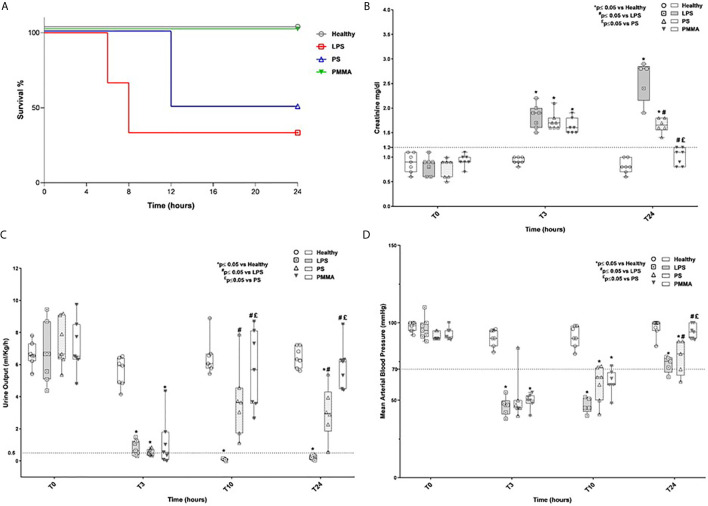
Figure 1.
Survival rate, renal function, oligo-anuria, and hypotension in a swine model of LPS-induced AKI. (A) Three animals (two animals of the LPS group and one animal of the PS group) died because of severe low blood pressure before completing the study protocol. (B, C) Endotoxemic pigs developed AKI with time-dependently increased creatinine serum levels and reduced urinary output. PMMA-CVVH treatment significantly reversed LPS effects (#p < 0.05 vs LPS, and £p < 0.05 vs PS). (D) After LPS infusion, animals presented hypotension and PMMA-CVVH treatment recovered MAP levels more than PS-CVVH treatment. (B–D) PS-CVVH treatment was no effective to recover creatine level, urine output, and arterial blood pressure to baseline median of healthy group. Data were obtained as described in the Methods section and expressed as median ± IQR of at least five pigs for each group (Healthy group and PMMA group, n = 7 for all time points; LPS group, T0-T3 n = 7, T10-T24 n = 5; PS group, T0-T3-T10 n = 7 and T24 n = 6). Statistically significant differences were assessed by the Mann–Whitney test (*p < 0.05 vs Healthy, #p < 0.05 vs LPS, and £p < 0.05 vs PS).