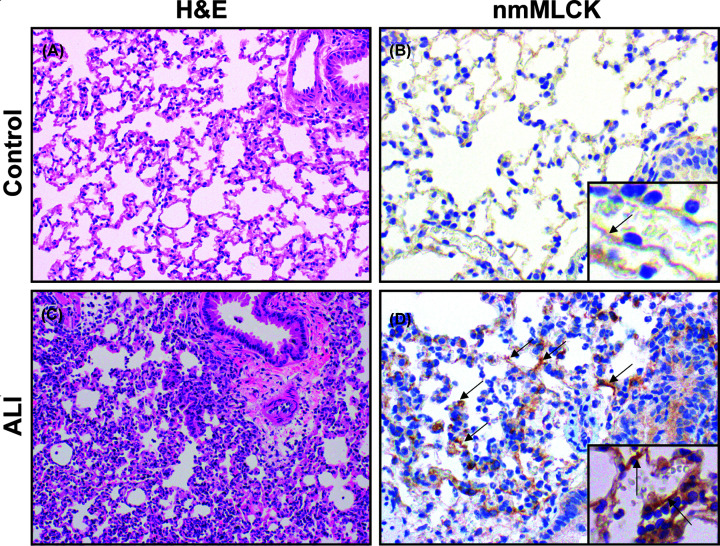
Figure 6. Increased nmMLCK protein expression in a preclinical murine ARDS model.
A well-established preclinical murine model of ARDS was utilized to assess nmMLCK protein expression. Mice were intratracheally injected with LPS 1 mg/kg (n=3) or PBS (controls) (n=3). After 18 h, mice were harvested, and lung tissue sections stained by Hematoxylin and Eosin with immunohistochemistry studies (IHC) performed with antibodies for nmMLCK proteins, which are specific for mouse, rat and human N-terminus of MYLK (sc-365352, Santa Cruz Biotechnology). (A,B) Control lungs from ice challenged with intratracheal PBS administration show normal H & E staining and histology (A) and weak IHC staining for nmMLCK (B). (C,D) H & E staining of lung tissues harvested from mice exposed to intratracheal LPS for 18 h, show significant acute lung inflammation and injury with interstitial and intra-alveolar neutrophil infiltration and fibrin deposition (C). IHC staining of LPS-exposed lung tissues also exhibited significant increases in nmMLCK immunoreactivity (D) including in lung ECs (arrows). (A,C) (×200); (B,D) (×400).