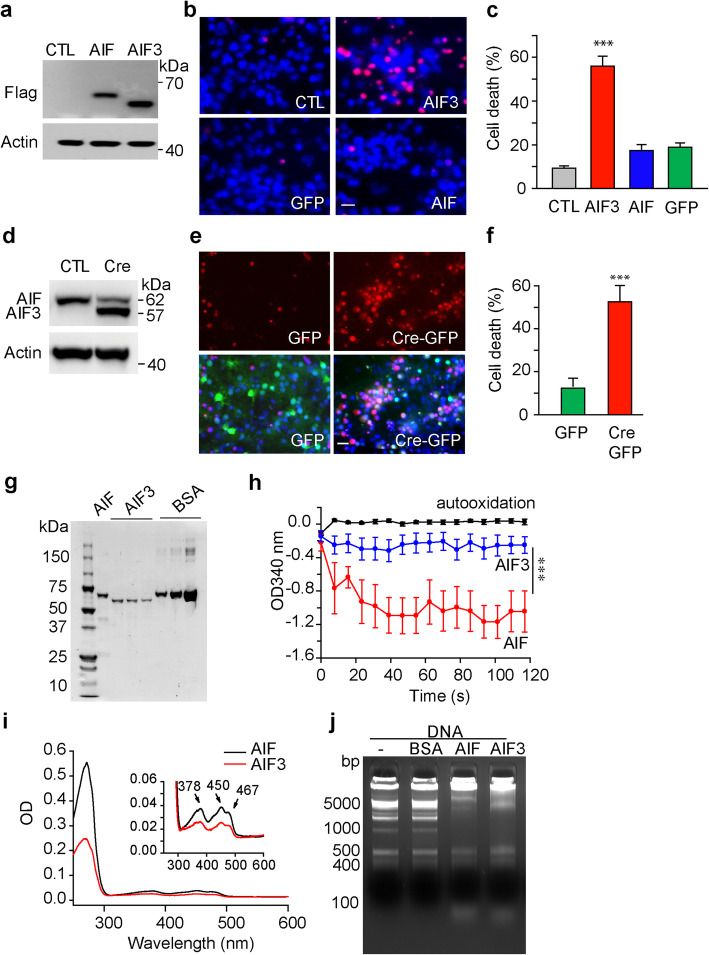
Fig. 8.
Characterization of AIF3 neurotoxicity effects in cortical neurons and its biochemical properties in vitro. a Expression of AIF and AIF3 in Hq cortical neurons 3 days after lentiviral transduction. b AIF3 expression in Hq cortical neurons caused neuronal death 4 days after lentiviral transduction as indicated by propidium iodide staining. Scale bar, 20 μm. c Quantification of AIF3-induced cytotoxicity in Hq cortical neurons 4 days after lentiviral transduction. Data were shown as mean ± S.E.M. n = 4. ***p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA. d Expression of AIF3 in AIF fl/fl cortical neurons 3 days after GFP or Cre-GFP lentiviral infection (1.0 × 109 T.U./ml). e AIF3 expression in AIFfl/Y/AIFfl/fl cortical neurons caused neuronal death 5 days after GFP or CRE-GFP lentiviral infection as indicated by propidium iodide staining. Scale bar, 20 μm. f Quantification of AIF3-induced cytotoxicity in cortical neurons 5 days after GFP or CRE-GFP lentiviral infection. Data are shown as mean ± S.E.M. n = 4. ***p < 0.001 by Student t test. g AIF (62 kDa) and AIF3 protein purification. BSA was used as purity and quantity control. h The NADH oxidase activity of purified AIF (3 μM) and AIF3 (3 μM) was determined by monitoring changes in absorbance at OD340 nm. Data were shown as mean ± S.E.M. n = 3. ***p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA. i FAD binding of purified AIF (1 μM) and AIF3 (1 μM) was determined by spectrophotometric wavelength scanning. j DNA retardation assay of purified AIF (3 μM) and AIF3 (3 μM) by incubating with 1 kb plus DNA ladder (200 ng) for 30 min. BSA was used as a negative control