Figure 3.
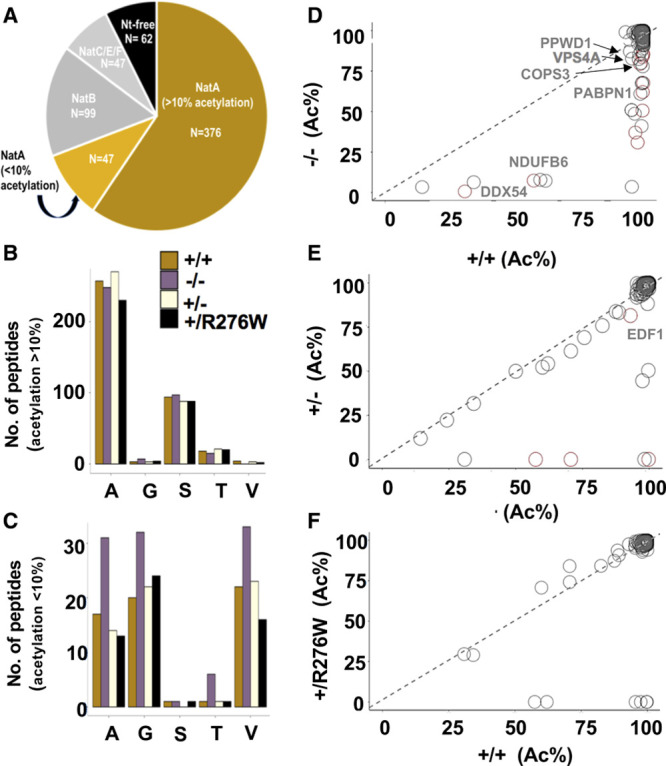
N-terminal acetylation in NAA15+/− and NAA15−/− induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). A, N-terminal peptides acetylated in NAA15+/+ iPSCs are categorized by NAT-type substrate specificity. NatA (N-terminal acetyltransferase) targets are displayed according to percent Nt-acetylation; Nt-acetylation >10% highlighted in gold and Nt-acetylation <10% highlighted in light gold. B and C, The number of Nt-acetylated NatA-type N-terminal peptides represented by residues A, G, S, T, or V in NAA15 mutant and wildtype iPSCs. Data is displayed as the absolute number of peptides measured from the sum of 2 biological replicates for each genotype. Alanine and serine residues are preferentially acetylated in peptides with >10% Nt-acetylation; glycine and valine residues are representative of N-termini with <10% Nt-acetylation. Primary peptide summary provided in Table V in the Data Supplement. There were no statistically significant differences between genotypes (hypergeometric test; data not shown). D–F, Representative scatter plots display the correlation of the degrees of Nt-acetylation of all N-termini identified as NatA targets in NAA15−/−, NAA15+/−, NAA15+/R276W, and NAA15+/+ iPSCs. Each plot compares NAA15 (N-alpha-acetyltransferase 15) mutant iPSCs to wildtype iPSCs. Differentially acetylated N-termini are found below the line of identity (y intercept=0, slope=1). Peptides lose acetylation moieties in NAA15-mutant iPSCs. NAA15−/− iPSCs have the largest number of peptides (n=32) with reduced Nt-acetylation. There are N-termini with reduced N-terminal acetylation in NAA15+/− iPSCs (n=9) and NAA15+/R276W iPSCs (n=8). Decreased protein expression changes are highlighted in red. COPS3 indicates COP9 signalosome complex subunit 3; DDX54, ATP-dependent RNA helicase; NDUFB6, NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1β subcomplex subunit 6; PABPN1, polyadenylate-binding protein 2; PPWD1, peptidyl-prolyl isomerase domain and WD repeat-containing protein 1; and VPS4A, vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 4.
