FIGURE 4.
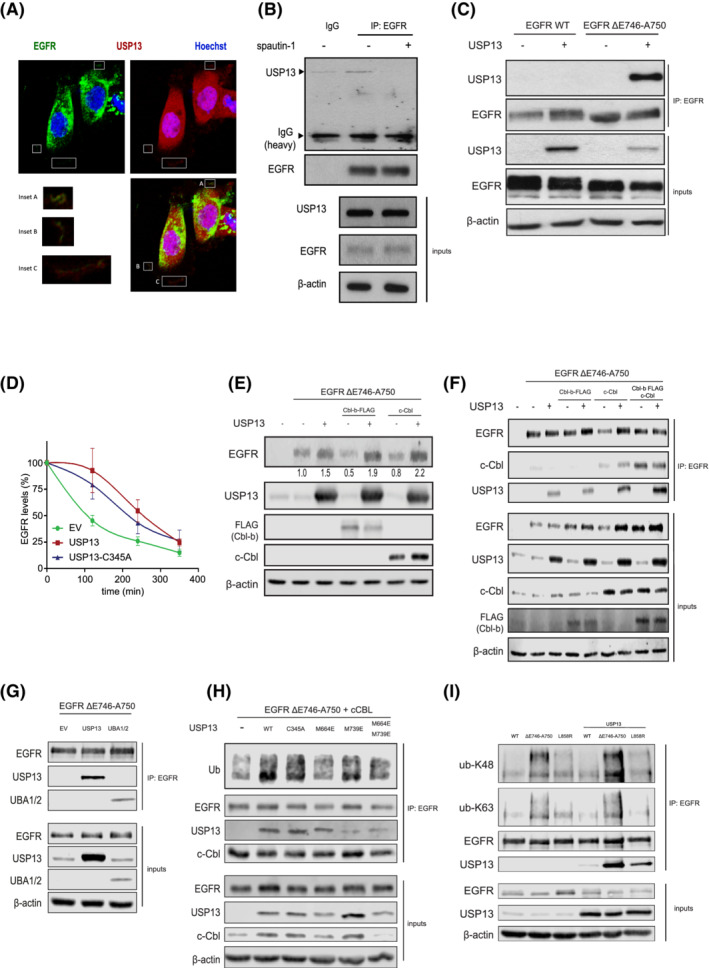
USP13‐EGFR interaction relies on c‐Cbl and the UBA domains of USP13. A, Confocal images of PC9 cells displaying localizations of USP13 (red), EGFR (green) and DNA (Hoechst, blue). Insets show colocalization of USP13 and EGFR. B, Immunoprecipitation (IP) of endogenous EGFR from PC9 cells treated with DMSO or spautin‐1 for 24 hours was analyzed by Western blotting as indicated. Inputs correspond to 5% of the sample used for IP. C, IP of EGFR from HEK293T cells overexpressing EGFR wild‐type (WT) or ΔE746‐A750 mutant and USP13. IP was performed 24 hours posttransfection. Samples were treated as in (B). D, EGFR degradation rates were determined by cycloheximide‐chase experiments and Western blotting. HEK293T cells were transfected with EGFR ΔE746‐A750 mutant and empty vector (EV), USP13 wild‐type or C345A mutant. Graph shows mean ± SEM. E, HEK293T cells were transfected with EGFR‐ΔE746‐A750, Cbl‐b, c‐Cbl and/or USP13. Cells were lysed 24 hours posttransfection and analyzed by Western blotting. F, IP of EGFR ΔE746‐A750 mutant from HEK293T cells also overexpressing Cbl‐b, c‐Cbl and/or USP13. Samples were treated as in E. G, As in (F) using HEK293T cells overexpressing USP13 full‐length or its UBA1/2 domains. H, As in (F) using HEK293T cells overexpressing USP13 wild‐type (WT) or mutants in its catalytic site (C345A), UBA1 (M664E) or UBA2 (M739E) domains (as indicated). I, IP of EGFR wild type, or mutants ΔE746‐A750 or L858R from HEK293T cells in the absence or presence of overexpressed USP13. IP product was immunoblotted using ubiquitin chain specifics K48 or K63 antibodies as indicated [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
