FIGURE 1.
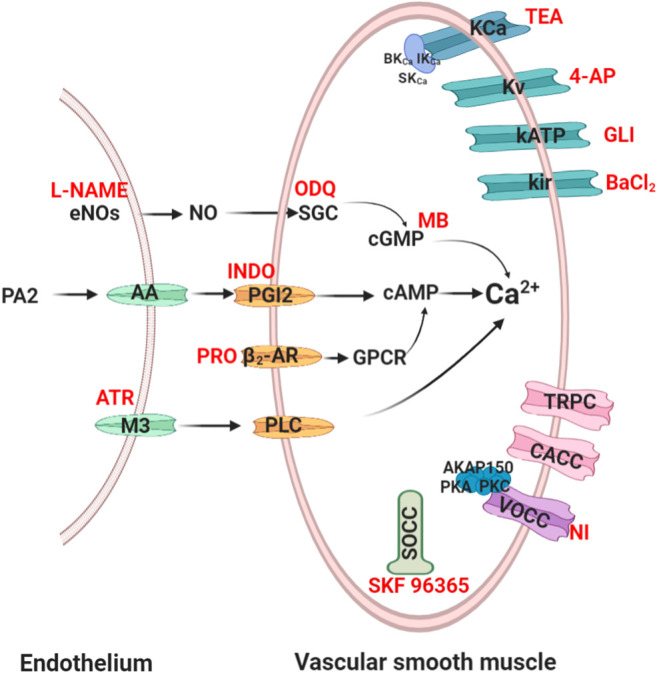
Routes of vasodilation mechanisms. Red words denote common blockers of the corresponding pathways. eNOs, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; SGC, soluble guanylyl cyclase; cGMP, cyclic 3′,5′-guanosine monophosphate; PA 2, phospholipase A 2; AA, arachidonic acid; PGI2, prostaglandin 2; cAMP, cyclic adenosine 3′, 5′-monophosphate; β2-AR, β2-adrenoreceptor; PLC, phospholipase C; L-NAME, nitro-L-arginine; ODQ, 1H- [1, 2, 4] oxadiazolo [4, 3-α] quinoxalin-1-one; MB, methylene blue; INDO, indomethacin; PRO, propranolol; ATR, atropine; NI, nifedipine; GLI, glibenclamide; 4-AP, 4-aminopyridine; TEA, tetraethylammonium.
