Figure 1.
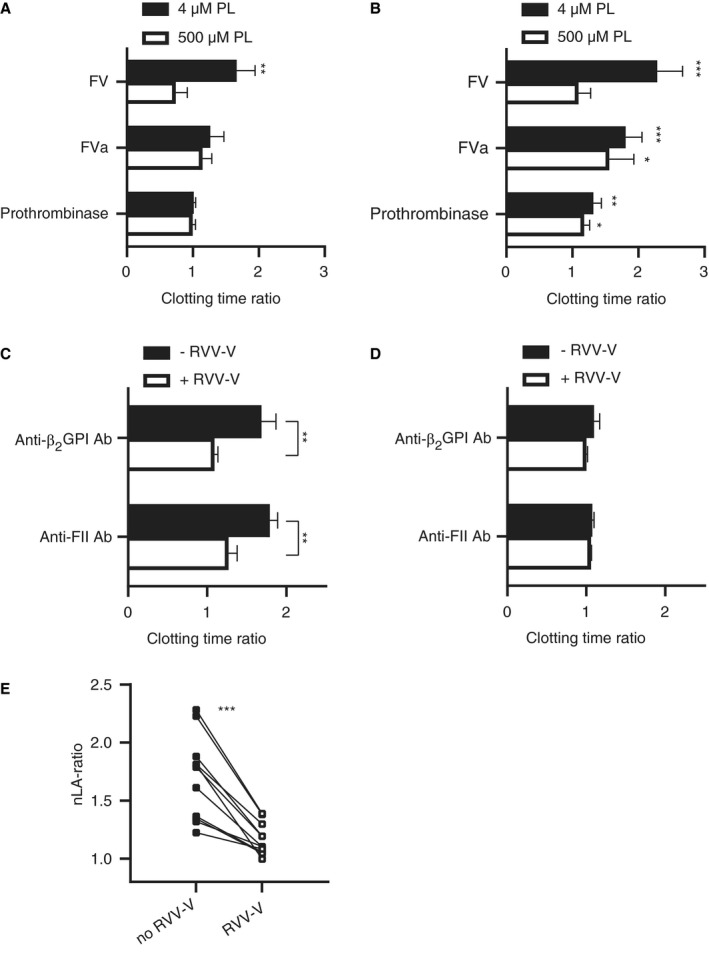
Lupus anticoagulant induced by anti‐beta2‐glycoprotein I (β2GPI) and anti‐prothrombin antibodies requires factor V (FV). A, B, FV‐depleted plasma was reconstituted with FV, activated FV (FVa), or preformed prothrombinase complex in the presence or absence of monoclonal anti‐β2GPI (3B7) (A) or anti‐prothrombin (anti‐FII; 28F4; B) antibodies. Clotting was initiated with activated factor X (FXa) and CaCl2 at 4 µM or 500 µM phospholipids. Clotting time ratios at low (4 µM) and high (500 µM) phospholipids were calculated between clotting times with and without monoclonal antibodies (mAbs; n = 4–5). Significant differences were determined between clotting times with and without mAbs using an unpaired Student’s t‐test. C, D, Pooled normal plasma was supplemented with the FV‐activating snake venom enzyme RVV‐V in the presence or absence of mAbs. Clotting times were obtained using dilute Russell's viper venom time (dRVVT) screen (C) and confirm (D) reagents and ratios were calculated between clotting times with and without mAbs (n = 3). Significant differences were determined between clotting time ratios with and without RVV‐V using an unpaired Student’s t‐test. E, Similar experiments were performed with mixed lupus anticoagulant (LA)‐positive patients plasma (n = 11) positive for anti‐β2GPI (n = 9) or anti‐prothrombin antibodies (n = 11). Results are shown as individual LA ratios of patients’ plasma incubated with or without RVV‐V and were calculated as described in the Method section. Connected lines represent paired data. Significant differences were determined using a paired sample t‐test. *P‐value<0.05, **P‐value<0.01, ***P‐value<0.005
