Figure 1.
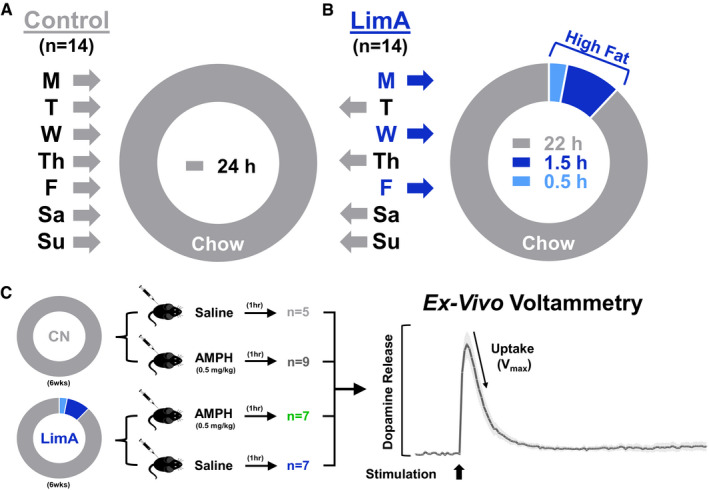
Experimental design. Mice were divided into two dietary groups: (A) the control (CN) group received standard rodent chow exclusively (n = 14), and (B) the limited‐access (LimA) group (n = 14) received 24‐hour access to standard chow on Tuesday (T), Thursday (Th), Saturday (Sa), and Sunday (Su) and limited access to a high‐fat diet for 2 hours on Monday (M), Wednesday (W), and Friday (F), with standard chow the remaining 22 hours on high‐fat days. (C) After 6 weeks on each feeding paradigm, mice from each group received 0.5 mg/kg of intraperitoneal amphetamine (AMPH) or an equal volume of saline 1 hour before proceeding to ex vivo voltammetry to measure dopamine release and uptake in the nucleus accumbens. Vmax, maximal rate of dopamine uptake.
