FIGURE 9.
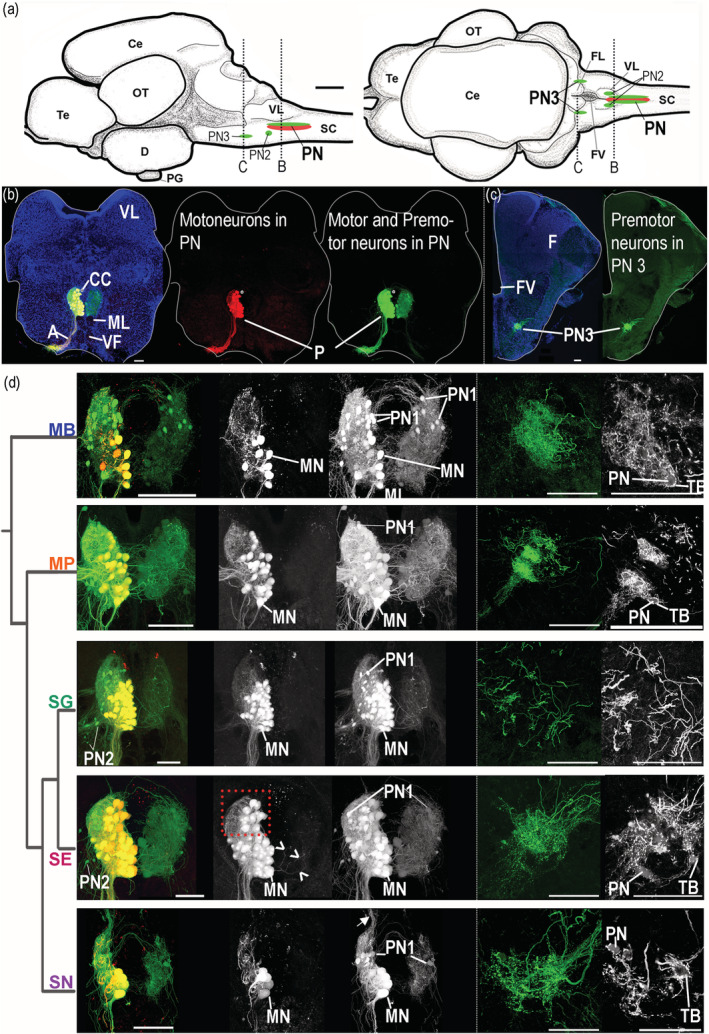
Protractor motor circuit of five mochokid catfish. Neurons labeled with dextran‐rhodamine and/or neurobiotin in Microsynodontis cf. batesii (MB), Mochokiella paynei (MP), Synodontis grandiops (SG), Synodontis eupterus (SE), and Synodontis nigriventris (SN). (a) Schematics of left sagittal and dorsal views of a S. grandiops brain showing the location of two protractor premotor populations that contain the PN2 or the PN3 and the protractor nucleus (PN) that contains motoneurons and PN1. (b) Photomicrographs of transverse hindbrain sections from S. grandiops showing the location of the PN. (c) Photomicrograph of transverse hindbrain section from S. eupterus showing the location of PN3. (d) Photomicrographs of transverse hindbrain sections showing PN and PN3 of the five mochokid species displayed according to their phylogenetic relationships, which was inferred from Day et al. (2013). A fluorescent piece of debris was removed from the Mi. cf. batesii image. Blue: 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (DAPI). Green: neurobiotin (N). Red: dextran rhodamine (D‐R). a, axons of the motoneurons; CC, central canal; Ce, cerebellum; D, diencephalon; FL, facial lobe; FV, fourth ventricle; MLF, medial longitudinal fasciculus; MN, protractor motoneuron; OT, optic tectum; PG, pituitary gland; Te, telencephalon; SC, spinal cord; TB, putative terminal bouton; VF, ventral fasciculus; VL, vagal lobe. Arrowheads for SE indicate labeled dendrites crossing the midline. Arrow for SN indicates labeled processes projecting dorsally. The dashed red frame highlights the dorsal part of the protractor nucleus of S. eupterus showing that this species had more motoneurons in this region. The dashed white frames highlighted the PN3 areas shown in the far right grayscale pictures. Note that fewer images were projected to produce these grayscale pictures allowing the observation of weakly labeled PN3 somata. White scale bar represents 100 μm for each species [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
