Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the cellular signaling pathways that lead to eIF4E phosphorylation.
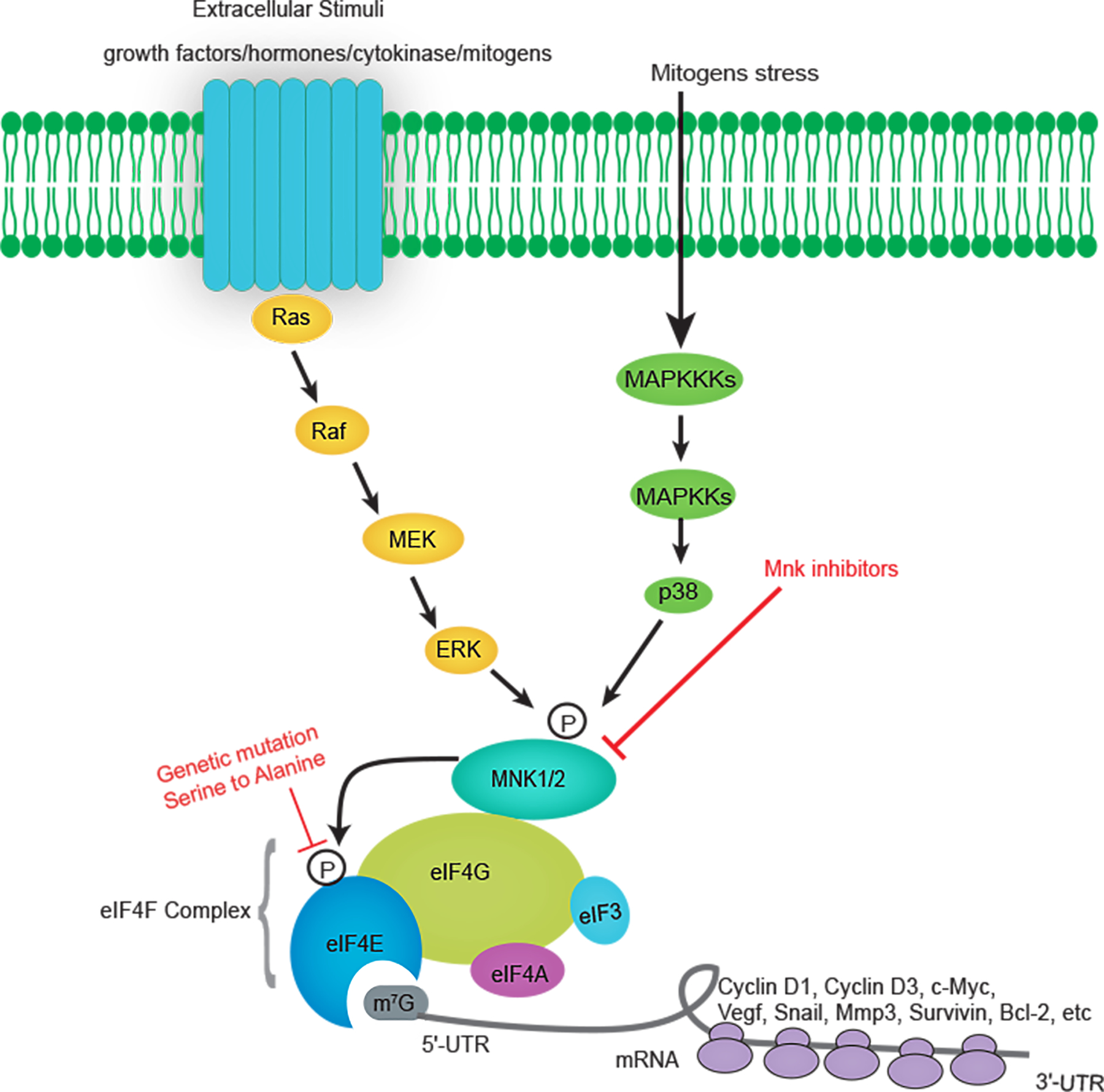
Extracellular stimuli and mitogens stress activate components of the MAPK pathway including the ERK and p38 MAP kinases. In turn, MNK1 and MNK2 are activated by ERK and p38 MAP kinases, bind to eIF4G and phosphorylate eIF4E at Ser209. Phosphorylation of eIF4E promotes mRNA translation of a variety of mRNAs involved in tumor biology, including Cyclin D1, Cyclin D3, C-myc, VEGF, SNAIL, MMP3, Survivin, Bcl-2, etc. As hyperphosphorylation of eIF4E is critical for its oncogenic activities, it can be repressed by genetic mutation of Ser209 or using MNK inhibitors.
