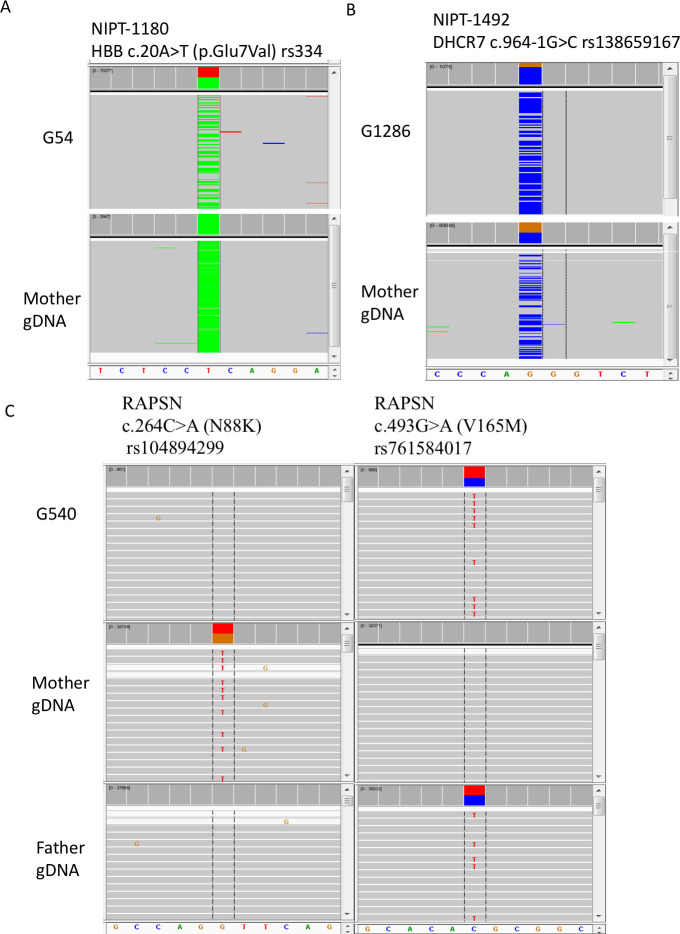
Fig 8. Genotyping for pathogenic variants in trophoblasts from three cases.
In panel A, the mother is affected and homozygous for the sickle cell anemia variant. Fetal trophoblast G54 is heterozygous for the variant (ClinGen Accession: CA125138). Reads for the mutant allele are colored green while reads for the normal allele are colored grey and summed in red. In panel B, the mother is heterozygous for a DHCR7 pathogenic variant that is also present in the father (CA090917). Fetal trophoblast G1286 is also heterozygous for the pathogenic variant, although there is biased over-representation of the variant allele. Reads for the mutant allele are colored blue while reads for the normal allele are colored grey and summed in brown. In panel C, the mother is heterozygous for the pathogenic N88K variant (CA199511) in the RAPSN gene, and the father is heterozygous for the V165M pathogenic variant (CA5976731). Fetal trophoblast G540 is heterozygous for the paternal V165K pathogenic variant but not for the maternal N88K pathogenic variant. Allele drop out for the N88K variant cannot be ruled out, and multiple cells must be tested to gain statistical evidence that the fetus has not inherited the N88K variant. All results agreed with data from amniocentesis or CVS. Data from NIPT case numbers 1180, 1492, and 1607.