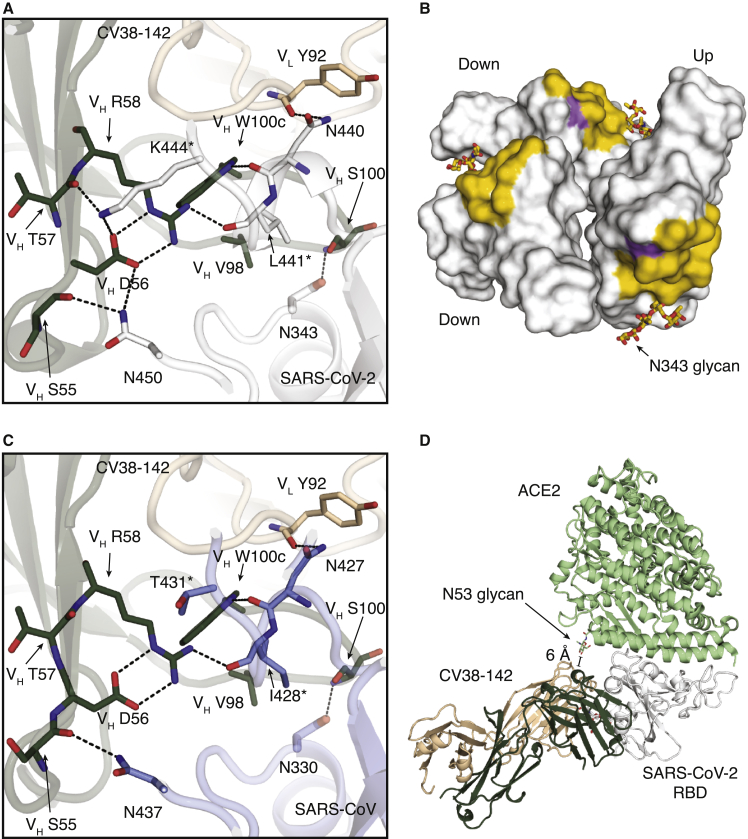
Figure 4.
Molecular interactions between CV38-142 and RBDs
SARS-CoV-2 RBD is in white, SARS-CoV RBD in pale blue, CV38-142 heavy chain in forest green and light chain in wheat, and ACE2 in pale green. Corresponding residues that differ between SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV are labeled with asterisks (∗). Dashed lines (black) represent hydrogen bonds or salt bridges.
(A) Direct interactions between CV38-142 and SARS-CoV-2 RBD are shown in sticks.
(B) Surface representation of the CV38-142 epitope site in SARS-CoV-2 RBD. The CV38-142 epitope is exposed to solvent regardless of whether the RBD is in the “up” or “down” state. RBDs are shown in surface representation model with symmetry derived from the spike protein (PDB: 6VYB) to show their solvent-accessible surface area in either “up” or “down” state. The buried surface area (BSA) was calculated by PISA program (Krissinel and Henrick, 2007). The epitope surface buried by the CV38-142 heavy chain is shown in orange and that by the light chain in purple. The total surface area buried on the RBD by CV38-142 is 792 Å2 with 629 Å2 (79%) contributed by the heavy chain and 163 Å2 (21%) by the light chain.
(C) Direct interactions between CV38-142 and SARS-CoV RBD. The same perspective is used as in (A).
(D) Structural alignment illustrating a model with simultaneous binding by CV38-142 and ACE2 to SARS-CoV-2 RBD. Structures of CV38-142 Fab + SARS-CoV-2 RBD and ACE2 + SARS-CoV-2 spike are aligned by superimposition of their RBD. The scale bar shows the closest distance between ACE2 and CV38-142, which is 6 Å, although some sugars in the N53 glycan are not visible in the electron density map.
See also Figures S3 and S5 and Table S2.