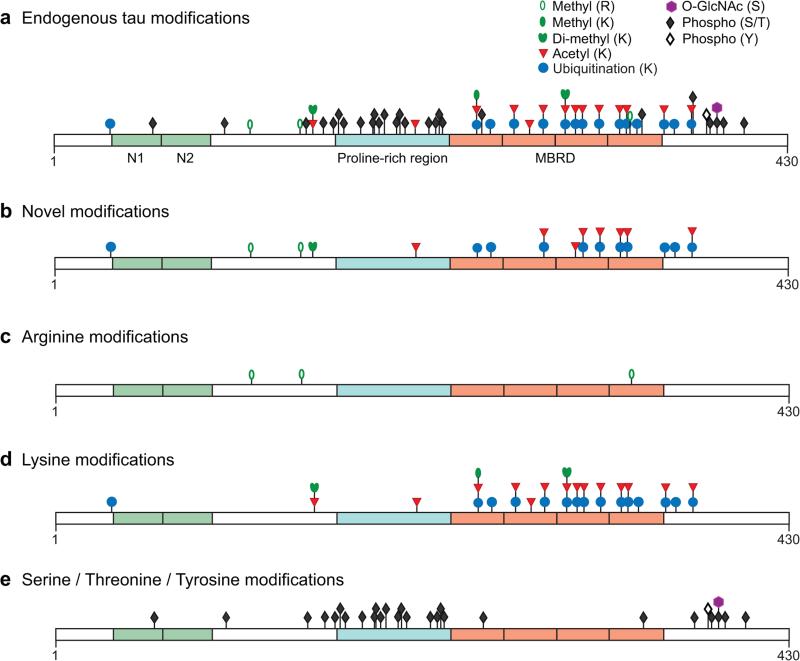
Figure 1.
PTMs identified in endogenous mouse tau. Mouse tau was isolated from brains of wildtype mice, and PTMs were assigned by mass spectrometry. Modifications are shown on the longest tau isoform expressed in the mouse central nervous system (430 amino acids). All assigned endogenous tau modifications are shown in the top panel (a). The lower panels show subsets of the same modifications, indicating those that are novel (b) or separating them by the amino acid modified: arginine (c), lysine (d), and serine/threonine/tyrosine (e). The N-terminal exons expressed in mouse tau 430 are shown in green, the proline-rich region in teal, and the four microtubule-binding repeats in orange. Only PTMs with unambiguously assigned sites from wildtype mice (Table 2) are indicated, and all sites are positioned to scale. Note that some amino acid residues can be alternately modified and that these modifications are mutually exclusive (e.g., ubiquitination, mono-/di-methylation, and acetylation). The N-terminal exons N1 and N2 are subject to alternative splicing.