Fig 4. NanB regulates nanA in a sialic acid-dependent manner.
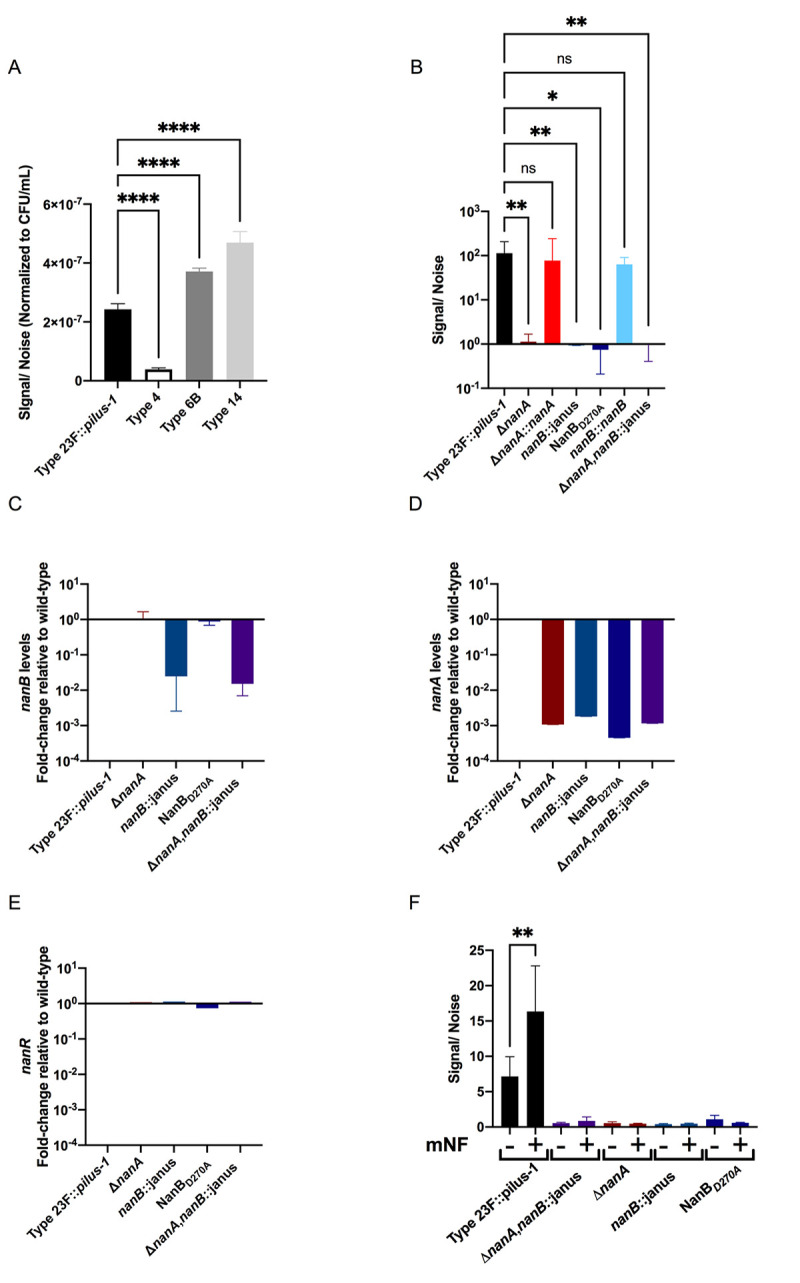
(A-B) Neuraminidase activity by Spn was quantified using NA-STAR kit (Thermo-Fischer Scientific, USA). Pneumococcal isolates of different serotypes (A), or the defined isogenic mutants of Type 23F::pilus-1 (B) were grown up to 1x108 CFU/mL, centrifuged and resuspended in PBS at a density of 107 CFU/mL. Bacterial suspensions were then sonicated (Amplitude, 8 μm) and the supernatant incubated in buffer and NA-STAR substrate for 20 min at room temperature before reading the chemiluminescent signal. To analyze the data, the signal was divided by the noise (PBS control). (A-B) Experiments were performed in duplicate and mean values of three independent experiments are shown with error bars corresponding to S.D.**,p<0.01; ****,p<0.0001 by ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test for multiple comparisons (C-E) Transcription level of nan genes was measured using quantitative RT-PCR. Spn strains were grown in TS at 37°C to OD620 = 1.0 followed by RNA extraction. Data shown as the fold-change was calculated relative to wild-type (Type 23F::pilus-1) for (C) nanB (D) nanA (E) nanR. Mean values of two independent experiments performed in duplicate are shown. (F) Neuraminidase levels and activity in response to sialic acid found in mNLs were also assessed using the NA-STAR kit. Type 23F::pilus-1 and isogenic mutants were grown in TS for 1hr, spun down and resuspended in DMEM. These samples were added at a 1:50 dilution to DMEM alone, or DMEM with mNL. They were incubated at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 3 hours, centrifuged and resuspended in PBS. Samples were then treated in the same manner as Fig 4B. The experiment was performed in duplicate and mean values of 3 independent experiments are shown with error bars corresponding to S.D.**,p<0.01 by an unpaired T-test to compare control to treatment.
