Fig 5. NanB and NanA mediate mucus evasion through removal of sialic acid.
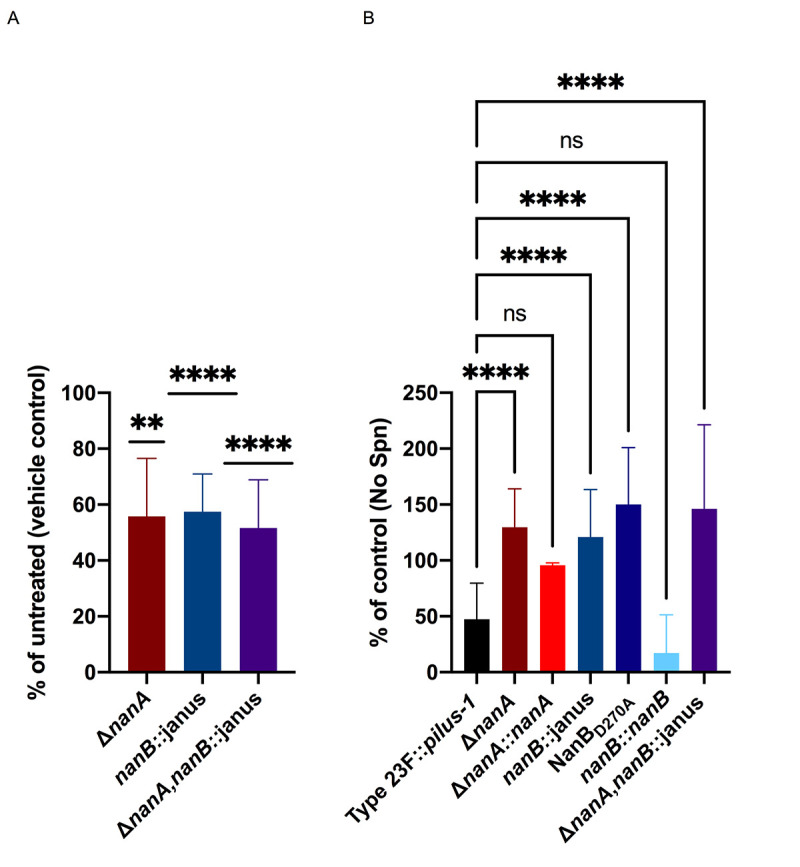
(A) Adherence of Type 23F::pilus-1 and isogenic mutants to pooled human nasal fluid (hNF) was assessed in a solid phase assay. Immobilized hNF (10μg) was pre-incubated with exogenous neuraminidase from lyophilized Vibrio cholerae or vehicle control (calcium saline) alone. (B) The ability of Type 23F::pilus-1 and isogenic mutants to remove sialic acid from mucus was quantified by ELISA. hNF was immobilized in a microtiter plate incubated with bacteria (1 x 106 CFU/100 μl DMEM) for 4hr at 37°C. Binding of biotinylated lectin Mal-I to α-2,3 sialic acid was detected using peroxidase-coupled streptavidin. The values of control wells without hNF were subtracted from each measured value. Results are illustrated as % of control of untreated hNF. (A-B) Experiments were performed in duplicates and mean values of three independent experiments are shown with error bars corresponding to S.D. **,p<0.01, ***; ****, p<0.0001. A one sample T test and Wilcoxon test to a theoretical mean of 1 (A) or a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test for multiple comparisons were used as statistical tests (B).
