Figure 8.
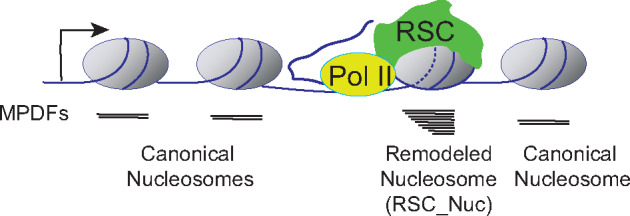
Model. According to this model, RSC targets the nucleosomes immediately downstream of the elongating RNA polymerase II (Pol II). The remodeling status of nucleosome is depicted by the dashed lines (–), and this nucleosome is in close proximity to Pol II. The nucleosome undergoing RSC-mediated remodeling will have DNA more accessible to MNase, yielding a heterogenous MNase protected DNA fragments (MPDFs) ranging from 80 to 160 bp compared to a shaper MPDF profile for canonical nucleosomes. The recruitment of RSC to the nucleosome could be facilitated by either direct interaction with Pol II (Soutourina et al.2006), or through phosphorylated C-terminal domain (CTD) of Pol II and transient acetylation by histone acetyltransferases SAGA and NuA4 (Govind et al.2007; Ginsburg et al.2009; Spain et al.2014). Resetting of the nucleosome to a canonical conformation can be achieved by rapid deacetylation by histone deacetylation complexes, such as Rpd3-small and Hos2-Set3C in a manner dependent on histone methylation (Carrozza et al.2005; Kim and Buratowski 2009; Govind et al.2010).
