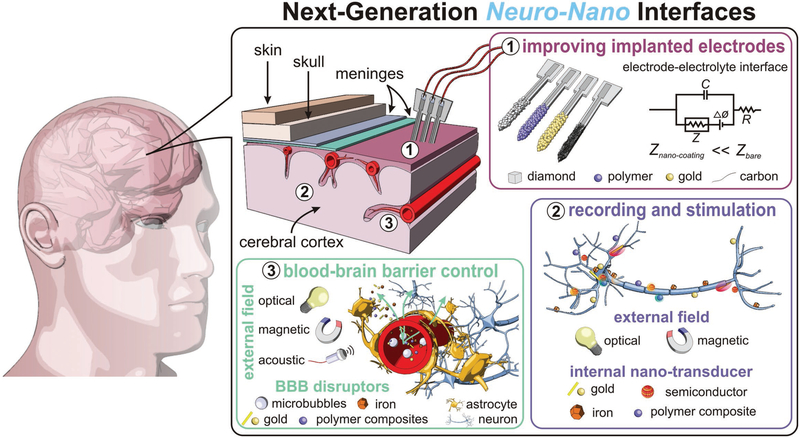
Figure 1.
Neural interfaces provide a window into the workings of the nervous system—enabling both biosignal recording and modulation. Nano-particles are used to improve current electrophysiological interfaces, as well as enable new nano-interfaces to modulate neural activity via alternative mechanisms. (i) Nanoparticle coatings of implanted electrodes reduce interface impedance with dramatically improved recording and stimulation fidelity. Alternatively, nanoparticles can be introduced intravenously and engineered to cross the blood brain barrier and excite neurons. (ii) Targeted-nanoparticles can remotely transduce external fields, e.g., infrared light or alternating magnetic fields, to modulate and stimulate neuronal function. (iii) An emerging, specialized use case for neural interfaces: Using nanoparticles and external fields to control the permeability of the blood-brain barrier for delivery of therapeutic and diagnostic materials into the central nervous system.