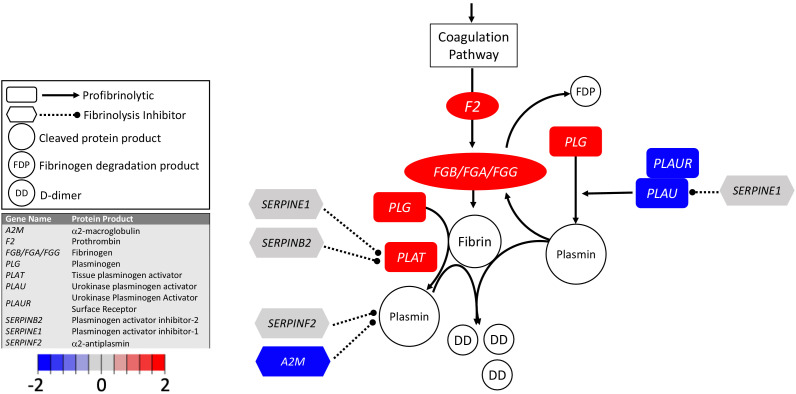
Figure 2. Transcriptional changes in lung induced by COVID-19 infection decreased PLAU and PLAUR, suggesting diminished fibrinolytic activity.
Figure shows differential gene expression (log2 fold change) of fibrinolytic pathway transcripts in BALF of COVID-19 patients; the image illustrates mechanistic relationships of the protein products of the identified transcripts during fibrinolysis. Shading indicates relative expression in COVID-19 patients compared to controls: increased (red) or decreased (blue). There was a moderate increase in PLAT (encoding tPA). There was also enhanced expression of FGB, FGA, and FGG (encoding fibrinogen chains) and decreased expression of PLAU and PLAUR (encoding uPA and uPAR, respectively). Other transcripts showing changes (e.g., F2, PLG) encode proteins typically produced in the liver; local expression of these proteins is unclear.