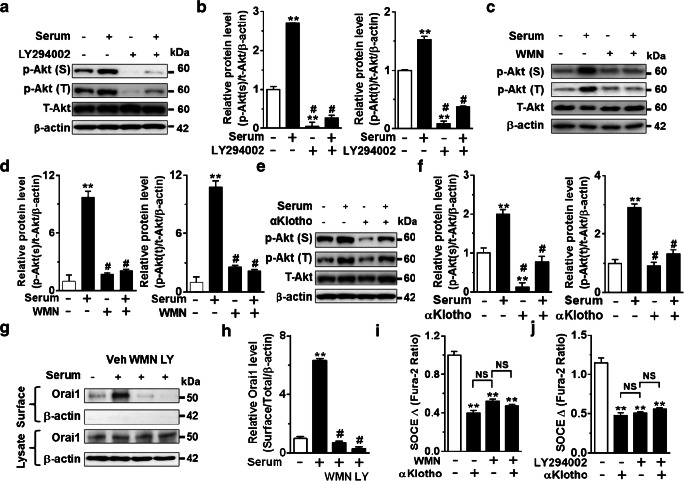
Fig. 5.
αKlotho inhibits SOCE and cell membrane abundance of Orai1 via the PI3K-dependent signaling pathway. a, c, and e Representative immunoblotting showing that effect of preincubation of PI3K inhibitors. a LY294002 (LY, 10 μM for 1 h) and c wortmannin (WMN, 50 nM for 1 h) and e recombinant αKlotho protein (1 nM for 1 h) on Akt phosphorylation at serine473 (p-Akt (S)) and threonine308 (p-Akt (T)) by serum stimulation (10%, 1 h). b, d, and f Quantification of Akt phosphorylation levels in panel a, c, and e respectively. **p < 0.01 vs. serum deprivation (SD) and #p < 0.01 vs. serum incubation. g Representative biotinylation assay showing the effect of PI3K inhibitors (WMN and LY) on the cell-surface expression of Orai1 by serum stimulation. h Summary of the surface Orai1 level in panel g. **p < 0.01 vs. SD and #p < 0.01 vs. serum treated. i and j Summary of SOCE traces showing that αKlotho suppressed SOCE and prevented the inhibition by preincubation of PI3K inhibitors, wortmannin (WMN, n = 40–186 each group) or LY294002 (LY, n = 76–188 each group), respectively. **p < 0.01 vs. vehicle. NS, not significant between each group. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA in b, d, f, and h–j