Figure 2. Cerebral malaria pathogenesis.
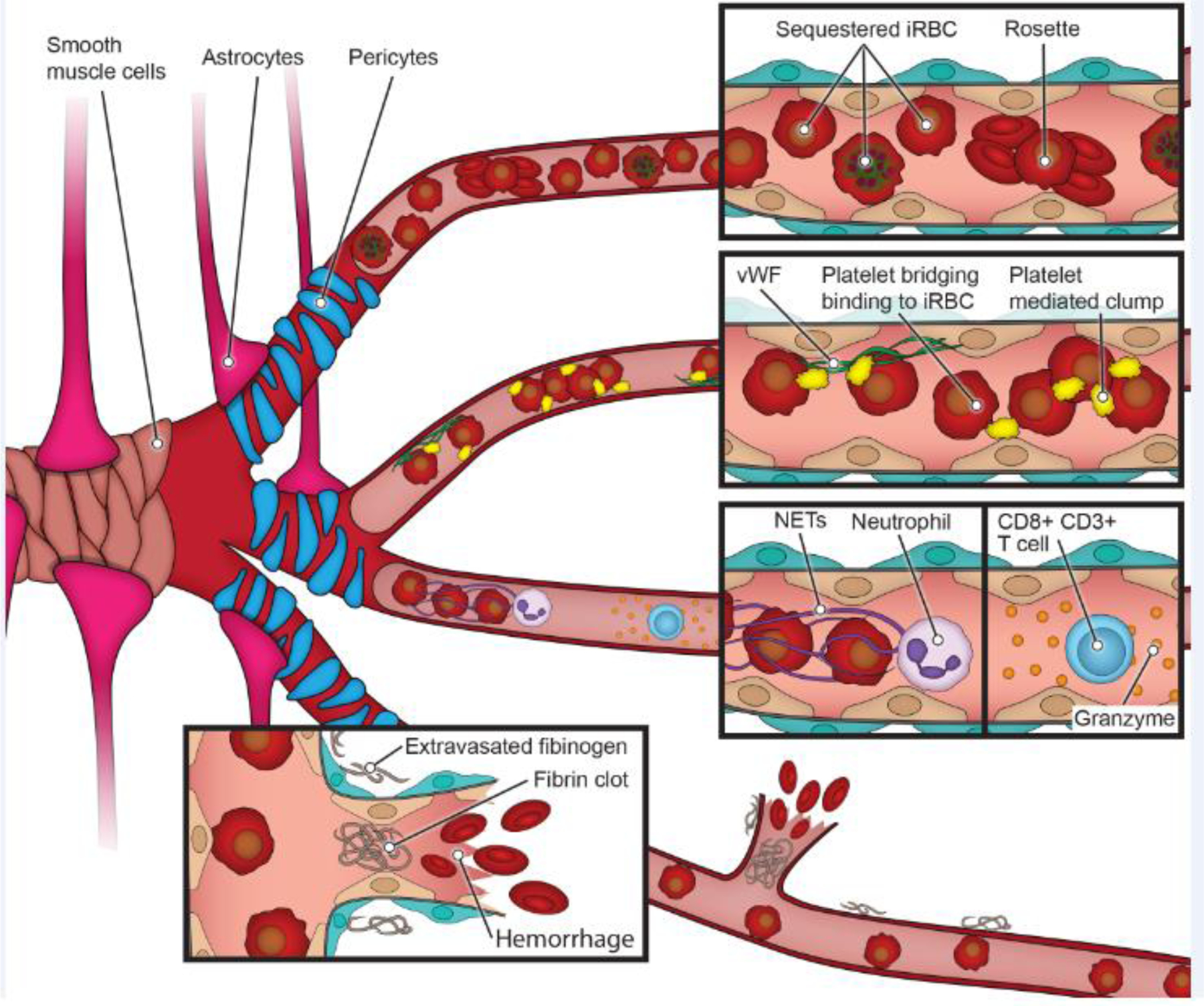
The unique properties of the BBB are achieved through interactions between endothelial cells, perivascular cells (smooth muscle cells in larger vessels and pericytes in the microvasculature) and astrocytes. P. falciparum sequestration in the brain microvasculature is a hallmark of CM and contributes to microvascular obstruction, probably along with rosettes, aggregates of iRBC to uninfected red blood cells. In autopsy studies, BBB disruption is exemplified by ring hemorrhages or fibrinogen deposition in the extravascular space. Platelets might also contribute to CM pathogenesis by bridging iRBC to vWF or endothelium or causing platelet-mediated iRBC clumps. Other cell types implicated in disease are neutrophils and CD8+ T cells. These pathogenic findings are sometimes localized in distinct regions of the brain, such as the white and grey matter [44].
